What is Budget? definition, features and classification
Zero-based budgeting is useful to identify and eliminate obsolete expenses. Suppose a company making construction equipment implements a zero-based budgeting process calling for closer scrutiny of manufacturing department expenses.
MANAGE YOUR BUSINESS
While many companies would say that they do both, in reality the investment of time and money falls squarely in one approach or the other. Over time, the use of line item budgets creates valuable statistical information that demonstrates trends and opportunities to save money. For example, retailers who have higher labor expenses during the winter holiday months can use data from line item budgets to find ways to cut labor costs in less busy times of the year. If you have anirregular income (meaning income that comes in at different amounts or at different times, or both, on a regular basis)—don’t sweat it! It’s just as easy to make a plan for an irregular income as it is for a regular one.
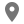
It projects a comprehensive picture of the proposed activities and anticipated results during the budget period. Though practices differ, a master budget generally includes, sales, production, costs-materials, labour, factory overhead, profit, appropriation of profit and major financial ratios. A budget is a financial statement of the estimated revenues and expenditures of an institution for a definite period of time. Obviously this is the best scenario, but even if you’re in this category, you’re not necessarily off the hook.
There is always room for improvement, particularly if you have a financial goal to meet like saving for further education or a vacation. Negotiated budgeting is a combination of both top-down and bottom-up budgeting methods. Executives may outline some of the targets they would like to hit, but at the same time, there is shared responsibility for budget preparation between managers and employees. Imposed budgeting is a top-down process where executives adhere to a goal that they set for the company.
Performance budgeting, for instance, is a useful model for routine processes that are easy to measure, such as paying invoices. Rather than automatically carrying a budget item forward, management must provide justification for each item before adding it to the budget, even if the prior budget included the item.
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
The focus is therefore in engaging the managers in the business more fully in the budget process, and building accountability for the results. The companies that adhere to this approach have their managers develop their own budgets.
However, it can be an extremely time-consuming approach, so many companies only use this approach occasionally. A budget is the sum of money allocated for a particular purpose and the summary of intended expenditures along with proposals for how to meet them. It may include a budget surplus, providing money for use at a future time, or a deficit in which expenses exceed income. A line item budget is a form of budget presentation that clusters proposed expenses by department or cost center. This method of aggregation more easily shows which departments and cost centers are absorbing the bulk of the entity’s funds.
Traditional budgeting analyzes only new expenditures, while ZBB starts from zero and calls for a justification of old, recurring expenses in addition to new expenditures. Zero-based budgeting aims to put the onus on managers to justify expenses, and aims to drive value for an organization by optimizing costs and not just revenue. Because of its detail-oriented nature, zero-based budgeting may be a rolling process done over several years, with a few functional areas reviewed at a time by managers or group leaders. Zero-based budgeting can help lower costs by avoiding blanket increases or decreases to a prior period’s budget. It is, however, a time-consuming process that takes much longer than traditional, cost-based budgeting.
A budget is a financial plan for a defined period, often one year. It may also include planned sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities, costs and expenses, assets, liabilities and cash flows. Companies, governments, families and other organizations use it to express strategic plans of activities or events in measurable terms. An organization may decide to consider alternatives to line item budgeting.
- First, it helps a business understand whether its income is sufficient to cover its expenses.
The Purposes, Advantages and Disadvantages of a Line Item Budget
What are the advantages of a line item budget?
A line item budget is a form of budget presentation that clusters proposed expenses by department or cost center. This method of aggregation more easily shows which departments and cost centers are absorbing the bulk of the entity’s funds.
Managers follow the goals and impose budget targets for activities and costs. It can be effective if a company is in a turnaround situation where they need to meet some difficult goals, but there might be very little goal congruence. Zero-based budgeting is best suited for addressing discretionary costs rather than essential operating costs.
The practice also favors areas that achieve direct revenues or production, as their contributions are more easily justifiable than in departments such as client service and research and development. Zero-based budgeting (ZBB) is a method of budgeting in which all expenses must be justified for each new period. The process of zero-based budgeting starts from a “zero base,” and every function within an organization is analyzed for its needs and costs. Budgets are then built around what is needed for the upcoming period, regardless of whether each budget is higher or lower than the previous one. Establishing a budget helps an organization allocate its resources for the coming fiscal period.
starts with the assumption that all department budgets are zero and must be rebuilt from scratch. Zero-based budgeting is very tight, aiming to avoid any and all expenditures that are not considered absolutely essential to the company’s successful (profitable) operation. This kind of bottom-up budgeting can be a highly effective way to “shake things up”. The other school of thought holds that it’s not about models, it’s about people. No matter how sophisticated models can get, the best information comes from the people in the business.
There are several methods and tools available for creating, using and adjusting a personal budget. For example, jobs are an income source, while bills and rent payments are expenses. A third category (other than income and expenses) may be assets (such as property, investments or other savings or value) representing a potential reserve for funds in case of budget shortfalls.
What is the difference between line item budget and program budget?
The line item budgeting system serves several purposes. First, it helps a business understand whether its income is sufficient to cover its expenses. Second, a line item budget makes it easy to verify when a single item exceeds the budget or comes in under budget.
BUSINESS PLAN
The company notices that the cost of certain parts used in its final products and outsourced to another manufacturer increases by 5% every year. The company has the capability to make those parts in-house using its own workers. After weighing the positives and negatives of in-house manufacturing, the company finds it can make the parts more cheaply than the outside supplier.
First, it helps a business understand whether its income is sufficient to cover its expenses. Second, a line item budget makes it easy to verify when a single item exceeds the budget or comes in under budget. For example, if a company suspects that its materials costs are getting out of hand, it can specifically pay attention to this item and compare the variance over time.
Articles
A personal budget or home budget is a finance plan that allocates future personal income towards expenses, savings and debt repayment. Past spending and personal debt are considered when creating a personal budget.
As the organization disburses funds, it traces its disbursements to the amounts it budgeted and adjusts the budget to meet unexpected expenses. Involving managers in the budgeting process helps managers understand the financial operations of the business and makes them accountable for their department’s expenditures. A line item budget is just one approach to making a budget, and there are numerous strengths and weaknesses of budgeting this way. Cash flow/cash budget – a prediction of future cash receipts and expenditures for a particular time period. The cash flow budget helps the business to determine when income will be sufficient to cover expenses and when the company will need to seek outside financing.