What is a bond sinking fund?
Bonds payable
A convertible bond is a fixed-income corporate debt security that yields interest payments, but can be converted into a predetermined number of common stock or equity shares. The conversion from the bond to stock can be done at certain times during the bond’s life and is usually at the discretion of the bondholder. Accounts payable are short-term liabilities relating to the purchases of goods and services incurred by a business. They generally are due within 30 to 60 days of invoicing, and businesses are usually not charged interest on the balance if payment is made in a timely fashion. Examples of accounts payable include accounting services, legal services, supplies, and utilities.
Companies looking to increase profits want to increase their receivables by selling their goods or services. Typically, companies practice accrual-based accounting, wherein they add the balance of accounts receivable to total revenue when building the balance sheet, even if the cash hasn’t been collected yet. In the same transaction, enter credits in the balance sheet equity accounts for common stock. Credit the common stock account for the par value of the shares created and the paid-in capital in excess of par account for the remainder of the converted bonds’ book value.
In most cases, it is the investor’s decision to convert the bonds to stock, although certain types of convertible bonds allow the issuing company to determine if and when bonds are converted. Companies benefit since they can issue debt at lower interest rates than with traditional bond offerings. Also, most convertible bonds are considered to be riskier/more volatile than typical fixed-income instruments. Issuing convertible bonds can help companies minimize negative investor sentiment that would surround equity issuance. Each time a company issues additional shares or equity, it adds to the number of shares outstanding and dilutes existing investor ownership.
Definition of Bonds Payable
It is typically used by lenders, investors, and creditors to estimate the liquidity of a business. The balance sheet is one of the documents included in an entity’s financial statements. Of the financial statements, the balance sheet is stated as of the end of the reporting period, while the income statement and statement of cash flows cover the entire reporting period. A deferred item, in accrual accounting, is any account where a revenue or expense, recorded as an liability or asset, is not realized until a future date (accounting period) or until a transaction is completed.
Bondholders can, then, convert into equity shares should the company perform well. The conversion price and ratio can be found in the bondindenture(in the case of convertible bonds) or in the securityprospectus(in the case of convertible preferred shares). The conversion price is the price per share at which a convertible security, such as corporate bonds or preferred shares, can be converted intocommon stock. The conversion price is set when the conversion ratio is decided for aconvertible security.
Common examples of expense payables are advertising, travel, entertainment, office supplies, and utilities. A/P is a form of credit that suppliers offer to their customers by allowing them to pay for a product or service after it has been received. Accounts payable is a liability since it’s money owed to creditors and is listed under current liabilities on the balance sheet. Current liabilities are short-term liabilities of a company, typically less than 90 days. Like all bonds, convertibles require you to pay back the face value at maturity.
Vouchered, or vouched, means that an invoice is approved for payment and has been recorded in the general ledger or A/P sub-ledger as an outstanding, or open, liability because it has not been paid. Payables are often categorized as trade payables, or purchases of physical goods that are recorded in inventory. Another category is expense payables, or purchases of goods or services that are expensed.
Accounts payable are monies that are owed to outside individuals and other businesses for goods and services provided. Accounts payable are usually a short-term liability, and are listed on a company’s balance sheet.
Bonds Payable Outline
Convertibles have a unique feature in that bondholders can exchange them for shares of your company’s common stock. When you issue the bond, you specify the terms and conditions that govern conversion, including the number of shares per bond and any waiting periods before conversion can occur. Using depreciation, a business expenses a portion of the asset’s value over each year of its useful life, instead of allocating the entire expense to the year in which the asset is purchased. This means that each year that the equipment or machinery is put to use, the cost associated with using up the asset is recorded. The rate at which a company chooses to depreciate its assets may result in a book value that differs from the current market value of the assets.
- Income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses (corporations or other legal entities).
- Expenses can vary; for example, corporate expenses related to fixed assets are usually deducted in full over their useful lives by using percentage rates based on the class of asset to which they belong.
Are bonds payable reported as a current liability if they mature in six months?
Expenses can vary; for example, corporate expenses related to fixed assets are usually deducted in full over their useful lives by using percentage rates based on the class of asset to which they belong. Accounting principles and tax rules about recognition of expenses and revenue will vary at times, giving rise to book-tax differences. If the book-tax difference is carried over more than a year, it is referred to as a deferred tax. Future assets and liabilities created by a deferred tax are reported on the balance sheet. Income tax payable can be accrued by debiting income tax expense and crediting income tax payable for the tax owed; the payable is disclosed in the current liability section until the tax is paid.
Accounts payable (A/P) is money owed by a business to its suppliers and creditors. In addition to its disclosure on the balance sheet, accounts payable is recorded in the A/P sub-ledger at the time an invoice is vouchered for payment.
Bond Discount with Straight-Line Amortization
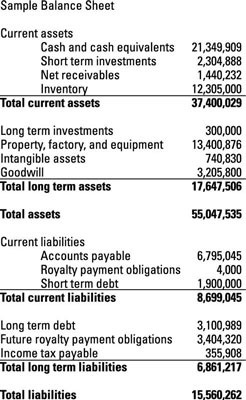
Accounts payable are usually reported in a business’ balance sheet under short-term liabilities. The exact set of line items included in a balance sheet will depend upon the types of business transactions with which an organization is involved. Usually, the line items used for the balance sheets of companies located in the same industry will be similar, since they all deal with the same types of transactions. The line items are presented in their order of liquidity, which means that the assets most easily convertible into cash are listed first, and those liabilities due for settlement soonest are listed first. The balance sheet is a report that summarizes all of an entity’s assets, liabilities, and equity as of a given point in time.
What are bonds payable in accounting?
Bonds payable is a liability account that contains the amount owed to bond holders by the issuer. This account typically appears within the long-term liabilities section of the balance sheet, since bonds typically mature in more than one year. Bonds are typically issued by larger corporations and governments.
A deferred revenue is specifically recognized when cash is received upfront for a product before delivery or for a service before rendering. In these cases, the earnings process is not complete when the cash is received, so the cash is recorded as a liability for the products or services that are due to the buyer. As a result, accounts receivable are assets since eventually, they will be converted to cash when the customer pays the company in exchange for the goods or services provided. Bonds that can be exchanged for a fixed number of shares of the company’s common stock.
Capital assets are significant pieces of property such as homes, cars, investment properties, stocks, bonds, and even collectibles or art. For businesses, a capital asset is an asset with a useful life longer than a year that is not intended for sale in the regular course of the business’s operation. For example, if one company buys a computer to use in its office, the computer is a capital asset. If another company buys the same computer to sell, it is considered inventory.
The liability accounts “bonds payable,” “discount on bonds payable” and “premium on bonds payable” record payment obligations. Convertible bonds can also affect the equity accounts “common stock” and “paid-in capital in excess of par” if a bondholder converts a bond to stock. Long-term liabilities are liabilities with a due date that extends over one year, such as a notes payable that matures in 2 years. In accounting, the long-term liabilities are shown on the right side of the balance sheet, along with the rest of the liability section, and their sources of funds are generally tied to capital assets.
If the deferred item relates to an expense (cash has been paid out), it is carried as an asset on the balance sheet. If the deferred item relates to revenue (cash has been received), it is carried as a liability.
Income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses (corporations or other legal entities). Corporate tax refers to a direct tax levied on the net earnings made by companies or associations and often includes the capital gains of a company.
Mandatory convertible bonds are required to be converted by the investor at a particular conversion ratio and price level. On the other hand, a reversible convertible bond gives the company the right to convert the bond to equity shares or keep the bond as a fixed income investment until maturity. If the bond is converted, it is done so at a preset price and conversion ratio. Asset accounts “cash” and “debt issue costs” reflect proceeds and expenses from issuing a bond. You also update the cash account when you repay the face value of a maturing bond.
Revenue is only increased when receivables are converted into cash inflows through the collection. Revenue represents the total income of a company before deducting expenses.