What are Audit Assertions? Balance Sheet and P&L assertions explained.
Examples include surprise cash counts, taking inventory, review and approval of accounting work, internal audits, peer reviews, and enforcement of job descriptions and expectations. Detective internal controls also help protect assets. For instance, if a cashier does not know when her cash drawer will be counted, she may be more likely to be honest. The auditor’s report contains the auditor’s opinion on whether a company’s financial statements comply with accounting standards.
Types of Audits
An unqualified, or clean, audit opinion means that the auditor has not identified any material misstatement as a result of his or her review of the financial statements. The term audit usually refers to a financial statement audit. A financial audit is an objective examination and evaluation of the financial statements of an organization to make sure that the financial records are a fair and accurate representation of the transactions they claim to represent. The audit can be conducted internally by employees of the organization or externally by an outside Certified Public Accountant (CPA) firm.
He is the author of The Little Book of Local Government Fraud Prevention and Preparation of Financial Statements & Compilation Engagements. Charles is the quality control partner for McNair, McLemore, Middlebrooks & Co. where he provides daily audit and accounting assistance to over 65 CPAs.
Detection risk is the chance that an auditor will fail to find material misstatements that exist in an entity’s financial statements. External auditors follow a set of standards different from that of the company or organization hiring them to do the work. The biggest difference between an internal and external audit is the concept of independence of the external auditor. Substantive procedures (or substantive tests) are those activities performed by the auditor to detect material misstatement or fraud at the assertion level. AMAS gathers information and performs audit testing in order to gain an understanding of internal controls; we examine documents and other records for evidence to determine whether effective internal controls are in place.
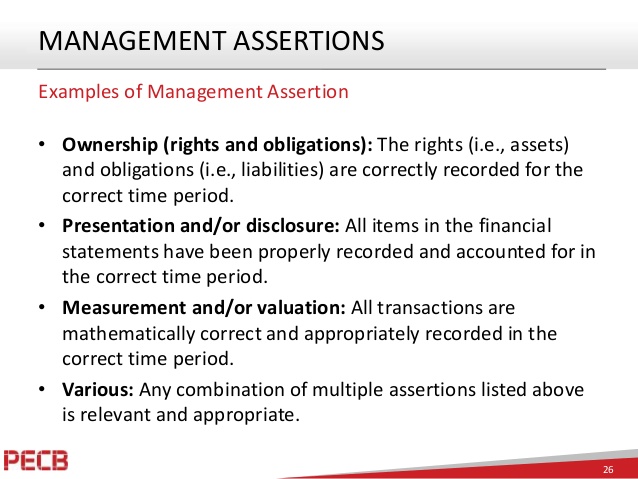
Management assertions in auditing
Management assertions or financial statement assertions are the implicit or explicit assertions that the preparer of financial statements (management) is making to its users. These assertions are relevant to auditors performing a financial statement audit in two ways. In developing that conclusion, the auditor evaluates whether audit evidence corroborates or contradicts financial statement assertions. Second, auditors are required to consider the risk of material misstatement through understanding the entity and its environment, including the entity’s internal control.
However, we only perform tests of controls if we intend to rely on the client’s internal controls to reduce the risk of material misstatement. Risk of material misstatement is the risk that the material misstatement can occur on financial statements and the internal controls can’t prevent or detect it. It is the combination of inherent risk and control risk.
An unqualified, or clean, auditor’s opinion provides financial statement users with confidence that the financials are both accurate and complete. External audits, therefore, allow stakeholders to make better, more informed decisions related to the company being audited. If the auditor is unable to obtain a letter containing management assertions from the senior management of a client, the auditor is unlikely to proceed with audit activities. One reason for not proceeding with an audit is that the inability to obtain a management assertions letter could be an indicator that management has engaged in fraud in producing the financial statements.
In the audit of revenue, we may assess the control risk as low in case that we believe that the internal controls are effective in preventing, detecting or correcting the material misstatements that can occur in the revenue account. Detective internal controls are designed to find errors after they have occurred. They serve as part of a checks-and-balances system and to determine how efficient policies are.
There are two types of substantive procedures related to auditing inventory. Substantive procedures are methods of verifying the actual numbers on financial statements. This is different from testing of controls, which are procedures that test the systems/policies that give rise to the numbers. External audits can include a review of both financial statements and a company’s internal controls.
The assertion that all the transactions and events recorded in the financial statements, have occurred and are related to the entity is called occurrence. A certification provided by the independent auditor of a company’s financial records that accompanies and opines on the audited financial statements. The results of the internal audit are used to make managerial changes and improvements to internal controls. The purpose of an internal audit is to ensure compliance with laws and regulations and to help maintain accurate and timely financial reporting and data collection. It also provides a benefit to management by identifying flaws in internal control or financial reporting prior to its review by external auditors.
An audit report is an appraisal of a small business’s complete financial status. Completed by an independent accounting professional, this document covers a company’s assets and liabilities, and presents the auditor’s educated assessment of the firm’s financial position and future.
What are the 7 audit assertions?
The assertion is that all business events to which the company was subjected were recorded. Cutoff. The assertion is that all transactions were recorded within the correct reporting period. The assertion is that recorded business transactions actually took place.
Financial statement assertions provide a framework to assess the risk of material misstatement in each significant account balance or class of transactions. Almost all companies receive a yearly audit of their financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
- Management assertions or financial statement assertions are the implicit or explicit assertions that the preparer of financial statements (management) is making to its users.
- These assertions are relevant to auditors performing a financial statement audit in two ways.
Like the audit of other financial statements line items, we perform substantive analytical procedures on revenue before performing the test of details. As auditors, we perform the audit of revenue by testing various audit assertions, including occurrence, completeness, accuracy, and cut-off. Among these assertions, the occurrence may be the most important assertion as material misstatement of revenue usually because of overstatement rather than understatement.
They present certain information in these financial statements. This information carries both explicit and implicit meanings. Management wants to tell the auditors that their revenues, as well as expenses, occurred actually and are complete, accurate, properly classified and recorded in the correct period. similarly, they also have certain audit assertions about the balance sheet and disclosure.We are going to cover each of them. Tests of details are used by auditors to collect evidence that the balances, disclosures, and underlying transactions associated with a client’s financial statements are correct.
The auditor will often request additional information and documents as needed. This is especially true if the client has incentives to overstate revenues. Charles Hall is a practicing CPA and Certified Fraud Examiner. For the last thirty years, he has primarily audited governments, nonprofits, and small businesses.
Audit
Lenders often require the results of an external audit annually as part of their debt covenants. For some companies, audits are a legal requirement due to the compelling incentives to intentionally misstate financial information in an attempt to commit fraud. As a result of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) of 2002, publicly traded companies must also receive an evaluation of the effectiveness of their internal controls. Audit Assertions are claims made by the management in their financial statements.These claims may be implicit (not directly stated but implied) or explicit (directly stated). You know, it is the responsibility of management to provide financial statements to external auditors.
What are the five audit assertions?
Definition. Audit Assertions are the implicit or explicit claims and representations made by the management responsible for the preparation of financial statements regarding the appropriateness of the various elements of financial statements and disclosures.
In addition, he consults with other CPA firms, assisting them with auditing and accounting issues. GAAP is a common set of accounting principles, standards, and procedures that public companies in the U.S. must follow when they compile their financial statements.
Management tells the auditor the financial statements show a true valuation of inventory – management are formally “asserting” this statement as being correct, so we call this at the “assertion level”. If the client’s internal control system is good, there is a reduced likelihood that there will be an error in the FS and the auditor will reduce the amount of audit work to be carried out. If the internal control system is poor, the auditor will have to perform much more work as the audit is the only defence left against a material misstatement appearing in the published FS.

Assertions are used by the auditors to assess misstatements and to obtain evidence. Audits performed by outside parties can be extremely helpful in removing any bias in reviewing the state of a company’s financials. Financial audits seek to identify if there are any material misstatements in the financial statements.
Audit reports are required by law if a company is publicly traded or in an industry regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Companies seeking funding, as well as those looking to improve internal controls, also find this information valuable. Audit Assertions are a representation by management that is embodied in the financial statements.

For example, an auditor could test the prepaid expenses asset account by examining each of the prepaid expenses that comprise the ending prepaid expenses balance. If sufficient appropriate audit evidence cannot be obtained, or the evidence points to a material misstatement in the FS, the auditor will have to issue a modified audit opinion. In this case, we need to perform test of control to obtain sufficient audit evidence to support our assessment.
Of these assertions, I believe existence, accuracy, and cutoff are most important. The audit client is asserting that the cash balance exists, that it’s accurate, and that only transactions within the period are included.