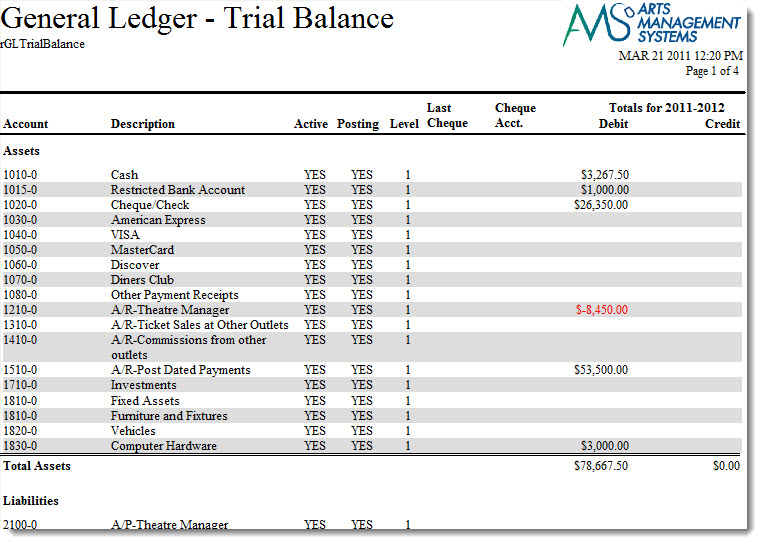
Trial Balance Definition
After the financials are prepared, the month end adjusting and closing entries are recorded (journalized) and posted to the appropriate accounts. After those entries are made, a post-closing trial balance is run. The post-closing trial balance verifies the debits equal the credits and that all beginning balances for permanent accounts are in place. It is important to note that just because the trial balance balances, does not mean that the accounts are correct or that mistakes did not occur. Nevertheless, once the trial balance is prepared and the debits and credits balance, the next step is to prepare the financial statements.
Why is it called a trial balance?
The trial balance is a type of financial report that is generated at the end of an accounting period, prior to the creation of your financial statements. Its main purpose is to allow you to catch any accounting errors and then make any necessary adjustments,so that your financial statements are completely accurate.
The Income Statement reports the total income and expenses of the business for the designated accounting period. The Balance Sheet is a snapshot of the business’s other account activity and an inventory of assets.

If the total debits equal the total credits, the trial balance is considered to be balanced, and there should be no mathematical errors in the ledgers. However, this does not mean there are no errors in a company’s accounting system. For example, transactions classified improperly or those simply missing from the system could still be material accounting errors that would not be detected by the trial balance procedure. The purpose of a trial balance is to prove that the value of all the debit value balances equals the total of all the credit value balances. If the total of the debit column does not equal the total value of the credit column then this would show that there is an error in the nominal ledger accounts.
The Statement of Owner’s Equity shows how much the business owners have tied up in the business and a valuation of the business at that particular time period. These statements are done monthly, but quarterly and annual statements are also computed. The trial balance is a report of every ledger account with a running balance for the time period selected. When transactions post to the ledger properly, your debit balances equal the credit balances, producing a net of zero.
Basic eCommerce Accounting Principles Small Business Owners Should Know
f the “debit DR” and “credit CR” balance totals do not match in the trial balance exercise, there is an accounting error somewhere in the account balances. The firm will try to find the mistakes responsible for the mismatch, and correct them, before publishing financial statements. During the trial balance period, accountants will also search for and try to fix other kinds of accounting errors that the trial balance does not reveal. The processing stage of the financial accounting cycle is the stage when things are recorded in the accounting system. General journal entries for business transactions are entered, and then those amounts are transferred to the general ledger.
Trial Balance is a part of the accounting process, that shows the debit and credit balances received from the ledger accounts. Whereas, the Balance Sheet is the statement that shows the company’s financial status by reviewing the capital, liabilities, and assets on a particular date. The trial balance is usually prepared by a bookkeeper or accountant. The bookkeeper/accountant used journals to record business transactions. The trial balance is a part of the double-entry bookkeeping system and uses the classic ‘T’ account format for presenting values.
Unadjusted vs. Adjusted Trial Balance
A company prepares a trial balance periodically, usually at the end of every reporting period. The general purpose of producing a trial balance is to ensure the entries in a company’s bookkeeping system are mathematically correct.
A trial balance only checks the sum of debits against the sum of credits. If debits do not equal credits then the accountant or bookkeeper must determine why. My “Cheat Sheet” Table begins by illustrating that source documents such as sales invoices and checks are analyzed and then recorded in Journals using debits and credits. The General Ledger Accounts are made up of Balance Sheet and Income Statement Accounts. Preparation of final accounts, income statements and balance sheets is the final stage of financial reporting.
Such uniformity guarantees there are no unequal debits and credits that have been incorrectly entered during the double-entry recording process. However, a trial balance cannot detect bookkeeping errors that are not simple mathematical mistakes. The trial balance is a list of debit and credit balances in the ledger accounts of a business at a given date. The debit and credit sides of trial balance must be equal to indicate that maintenance of the ledger accounts under the double entry system is accurate. However, the balancing of debit and credit balances doesn’t necessarily mean that the financial statements have no material errors.
Also, they must find and fix other material errors underlying the account balances during the trial balance period, as well. If a statement is prepared with debit balances in one side/column and credit balances on the other side/column, the totals of the two sides/columns will be equal. Or simply a trial balance may be defined as “a list of balances standing on the ledger accounts and cashbook of a concern”. Companies initially record their business transactions in bookkeeping accounts within the general ledger. Furthermore, some accounts may have been used to record multiple business transactions.
- The trial balance is a list of debit and credit balances in the ledger accounts of a business at a given date.
- Such uniformity guarantees there are no unequal debits and credits that have been incorrectly entered during the double-entry recording process.
This error must be found before a profit and loss statement and balance sheet can be produced. The debit and credit totals in the trial balance must match to build the new Income statement and Balance sheet correctly. Also, they must unearth and correct other material errors underlying the account balances during the trial balance period, as well.
At the end of an accounting period, the accounts of asset, expense or loss should each have a debit balance, and the accounts of liability, equity, revenue or gain should each have a credit balance. On a trial balance worksheet, all the debit balances form the left column, and all the credit balances form the right column, with the account titles placed to the far left of the two columns. It is during this stage that the financial reports a business uses the most – the Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Statement of Owner’s Equity – are completed. All required general journal entries have been completed, and the general ledger accounts have been tallied, adjusted and closed out. These numbers are then placed on their respective financial statements.
When the post-closing trial balance is run, the zero balance temporary accounts will not appear. However, all the other accounts having non-negative balances are listed, including the retained earnings account. As with the trial balance, the purpose of the post-closing trial balance is to ensure that debits equal credits. After determining, via the source documents, that an event is a business transaction, it is then entered into the company books via a journal entry.
The trial balance is prepared after all the transactions for the period have been journalized and posted to the General Ledger. The main aim of preparing a trial balance is to ensure that the bookkeeping system is mathematically correct. Prior to preparing the final accounts at the end of an accounting period, a trial balance is prepared to detect arithmetical errors.
The trial balance ensures that all the postings made to the ledger accounts do not contravene rules of double entry bookkeeping. Preparing a trial balance for a company serves to detect any mathematical errors that have occurred in the double-entry accounting system.
What is a trial balance and why is it important?
The purpose of a trial balance is to ensure that all entries made into an organization’s general ledger are properly balanced. A trial balance lists the ending balance in each general ledger account. The total dollar amount of the debits and credits in each accounting entry are supposed to match.
This is because some financial statement items may not be included in the ledger accounts, a mistake known as the error of omission. A trial balance is a list of all the general ledger accounts (both revenue and capital) contained in the ledger of a business. This list will contain the name of each nominal ledger account and the value of that nominal ledger balance.
What is a trial balance?
A trial balance is a list and total of all the debit and credit accounts for an entity for a given period – usually a month. The format of the trial balance is a two-column schedule with all the debit balances listed in one column and all the credit balances listed in the other.
Transfer of balances from the ledger accounts to the trial balance occurs at the end of the accounting period. The income statement and balance sheet are then prepared using the account balances indicated in the trial balance. A trial balance is a bookkeeping worksheet in which the balance of all ledgers are compiled into debit and credit account column totals that are equal.
Guide to Fiscal Year-End Checklist For Small Business Owners
It is prepared after all of that period’s business transactions have been posted to the General Ledger via journal entries. The post-closing trial balance can only be prepared after each closing entry has been posted to the General Ledger. The purpose of closing entries is to transfer the balances of the temporary accounts (expenses, revenues, gains, etc.) to the retained earnings account. After the closing entries are posted, these temporary accounts will have a zero balance. The permanent balance sheet accounts will appear on the post-closing trial balance with their balances.
After all the transactions for the period have been entered into the appropriate journals, the journals are posted to the general ledger. The trial balance proves that the books are in balance or that the debits equal the credits. From the trial balance, a company can prepare their financial statements.
AccountingTools
So, if a business had cash sales of $350, the journal entry would include a debit to Cash and a credit to Sales, with general ledger entries to update each account. Once all the accounting transactions have been recorded into the general journal and general ledger accounts, the ledgers are totaled and the unadjusted trial balance is created. The ending balances of all accounts of an entity for a given financial period are summarized in the trial balance. To ensure that the balances of the various business accounts are correct, the debit and credit totals must be equal. If this is not the case, then some of the individual accounts are incorrect and hence you must carry out adjustments to address this anomaly.
Each nominal ledger account will hold either a debit balance or a credit balance. The debit balance values will be listed in the debit column of the trial balance and the credit value balance will be listed in the credit column. The trading profit and loss statement and balance sheet and other financial reports can then be produced using the ledger accounts listed on the same balance. The post-closing trial balance is the last step in the accounting cycle.