The Effects of Accounts Receivable on a Balance Sheet

Example of Accounts Receivable
If the ratio is declining over time, it means that the company is having increasing difficulty collecting cash from its customers, which could lead to financial problems. The accounts receivable item on your balance sheet does not represent a liquid asset. Payment of the receivable is outside of your control until your customer’s payment clears. For that reason, you list receivables after cash and short-term investments, which you can quickly convert to cash. Following accounts receivable on the asset side is inventory, which includes product that you have available for sale and which remains on the balance sheet until you sell it.
Is account receivable credit or debit?
Accounts receivable is the amount owed to a seller by a customer. As such, it is an asset, since it is convertible to cash on a future date. Accounts receivable is listed as a current asset in the balance sheet, since it is usually convertible into cash in less than one year.
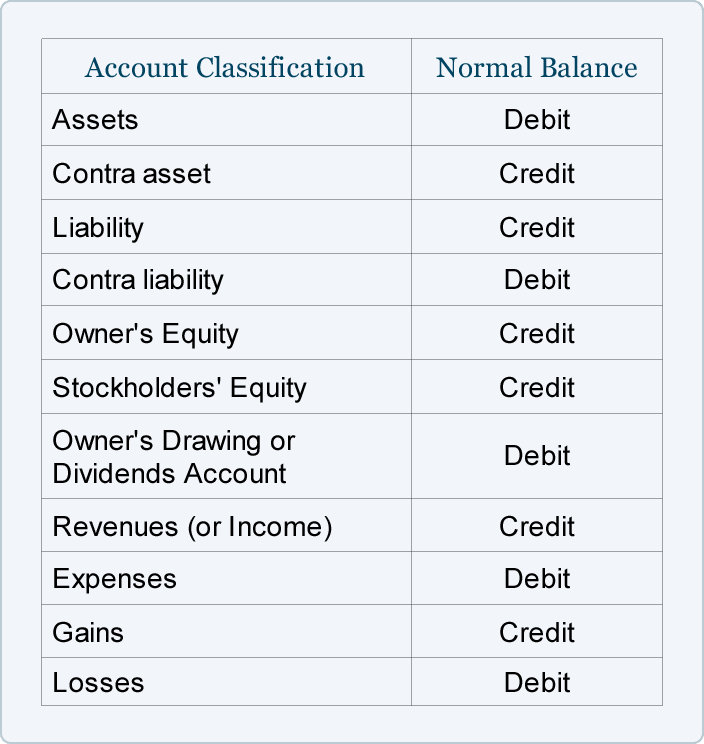
Debits and Credits Outline
The rate at which a company chooses to depreciate its assets may result in a book value that differs from the current market value of the assets. In addition, all the expenses along the way of creating the intangible asset are expensed. However, intangible assets created by a company do not appear on the balance sheet and have no recorded book value.
Assets such as bank deposits, accounts receivable, and long-term investments in bonds and stocks lack physical substance, but are not classified as intangible assets. These assets are financial instruments and derive their value from the right or claim to receive cash or cash equivalents in the future. Companies record accounts receivable as assets on their balance sheets since there is a legal obligation for the customer to pay the debt. Furthermore, accounts receivable are current assets, meaning the account balance is due from the debtor in one year or less. If a company has receivables, this means it has made a sale on credit but has yet to collect the money from the purchaser.
Accounts receivable — money that individuals or other businesses owe you — count as an asset. The individual receivables move up or down the balance sheet depending on when, and if, they are paid. Using depreciation, a business expenses a portion of the asset’s value over each year of its useful life, instead of allocating the entire expense to the year in which the asset is purchased. This means that each year that the equipment or machinery is put to use, the cost associated with using up the asset is recorded.
Essentially, the company has accepted a short-term IOU from its client. Accounts receivable (AR) is the balance of money due to a firm for goods or services delivered or used but not yet paid for by customers.
Accounts receivables are listed on the balance sheet as a current asset. AR is any amount of money owed by customers for purchases made on credit. Anyone analyzing the results of a business should compare the ending accounts receivable balance to revenue, and plot this ratio on a trend line.
Because of this, when a company is purchased, often the purchase price is above the book valueof assets on the balance sheet. The purchasing company records the premium paid as an intangible asset on its balance sheet. There are five main types of accounts in accounting, namely assets, liabilities, equity, revenue and expenses.
“Temporary accounts” (or “nominal accounts”) include all of the revenue accounts, expense accounts, the owner’s drawing account, and the income summary account. Generally speaking, the balances in temporary accounts increase throughout the accounting year. At the end of the accounting year the balances will be transferred to the owner’s capital account or to a corporation’s retained earnings account. Expenses normally have debit balances that are increased with a debit entry.
What type of account is accounts receivable?
Accounts Receivable is an asset account and is increased with a debit; Service Revenues is increased with a credit.
We now offer eight Certificates of Achievement for Introductory Accounting and Bookkeeping. The certificates include Debits and Credits, Adjusting Entries, Financial Statements, Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, Working Capital and Liquidity, and Payroll Accounting.
Some costs with respect to intangible assets must be capitalized rather than treated as deductible expenses. Treasury regulations generally require capitalization of costs associated with acquiring, creating, or enhancing intangible assets.
- When you draw up a balance sheet, you’re taking a financial snapshot of your business.
If the account goes unpaid, at some point you will have to change its status. The balance sheet should include an allowance for doubtful accounts, which is subtracted from the accounts receivable amount.
The general rule is that if the acquired property’s useful life is longer than the taxable year, then the cost must be capitalized. The capital expenditure costs are then amortized or depreciated over the life of the asset. Choice of the appropriate accounting treatment for such costs should be guided by the degree of certainty of future benefits and the principle of matching revenues and expenses. Accounts receivable is an important aspect of a businesses’ fundamental analysis.
Intangible assets created by a company do not appear on the balance sheet and have no recorded book value. Examples of tangible assets include desktop computers, laptops, cars, cash, equipment, buildings and more. Your trademark, logo, copyrights and other non-physical items are considered intangible assets. Asset accounts, for example, can be divided into cash, supplies, equipment, deferred expenses and more.
When you draw up a balance sheet, you’re taking a financial snapshot of your business. The balance sheet shows current assets and liabilities, and any equity remaining for the owner and/or shareholders.
Their role is to define how your company’s money is spent or received. The accounting for intangible assets depends on whether the intangible has a limited or an indefinite life. The costs of acquiring and defending a copyright may be capitalized, but the research and development costs involved must be expensed as incurred. Generally, the useful life of the copyright is less than its legal life.
Is accounts receivable an asset or revenue?
Since expenses are usually increasing, think “debit” when expenses are incurred. If the receivable amount only converts to cash in more than one year, it is instead recorded as a long-term asset on the balance sheet (possibly as a note receivable). The IRS requires that businesses use one accounting system and stick to it (see below for an exception).
Most businesses allow 30, 60 or 90 days, depending on the relationship with the customer and the size of the order. The receivable remains on the balance sheet until it is paid, at which time the amount received joins your cash on the asset side. Any outstanding amounts your customers owe you remain as receivables, but only for a limited time. For example, a business may create a mailing list of clients or establish a patent. If a business creates an intangible asset, it can write off the expenses from the process, such as filing the patent application, hiring a lawyer, and paying other related costs.
For example, an amount paid to obtain a trademark must be capitalized. Certain amounts paid to facilitate these transactions are also capitalized. Some types of intangible assets are categorized based on whether the asset is acquired from another party or created by the taxpayer. The regulations contain many provisions intended to make it easier to determine when capitalization is required.
Revenues and gains are recorded in accounts such as Sales, Service Revenues, Interest Revenues (or Interest Income), and Gain on Sale of Assets. These accounts normally have credit balances that are increased with a credit entry. If you sell a product or service on credit, you generate a receivable. Each receivable has a term, which is the period you’ve extended to the buyer for payment.
Accounts receivable is a current asset so it measures a company’s liquidity or ability to cover short-term obligations without additional cash flows. Accounts receivable refers to the outstanding invoices a company has or the money clients owe the company. The phrase refers to accounts a business has the right to receive because it has delivered a product or service. Accounts receivable, or receivables represent a line of credit extended by a company and normally have terms that require payments due within a relatively short time period. Accounts receivable is an asset account on the balance sheet that represents money due to a company in the short-term.
Permanent and Temporary Accounts
You can also sell the receivable to another business such as a collection agency. The agency will pay an agreed percentage for the receivable or agree to a partial payment if and when the debt is collected. Expenses are matched to revenue in accrual accounting, meaning they’re recorded at the same time as revenue.
Research and development (R&D) costs are not in and of themselves intangible assets. R&D activities frequently result in the development of something that is patented or copyrighted (such as a new product, process, idea, formula, composition, or literary work). Many businesses spend considerable sums of money on research and development to create new products or processes, improve present products, and discover new knowledge that may be valuable. A cost which cannot be deducted in the year in which it is paid or incurred must be capitalized.
At some point you will have to write off the sale amount if your customer doesn’t remit payment. This means transferring money from any reserve you have set up for unpaid accounts to cover the loss.
So if a house painter has to buy paint for a job, the total income for the job and the cost of the paint are recorded in the books at same time. DebitCreditCash10,000Accounts Receivable25,000Interest Receivable600Supplies1,500Prepaid Insurance2,200Trucks40,000Accum. The other main type of account is the permanent account, in which balances are retained on an ongoing basis. These accounts are aggregated into the balance sheet, and include transactions related to assets, liabilities, and equity. Intangible assets only appear on the balance sheet if they have been acquired.
The costs of the copyright should be allocated to the years in which the benefits are expected to be received. The difficulty of determining the number of years over which benefits will be received normally encourages the company to write these costs off over a fairly short period of time. When a business purchases capital assets, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers the purchase a capital expense. In most cases, businesses can deduct expenses incurred during a tax year from their revenue collected during the same tax year, and report the difference as their business income. However, most capital expenses cannot be claimed in the year of purchase, but instead must be capitalized as an asset and written off to expense incrementally over a number of years.