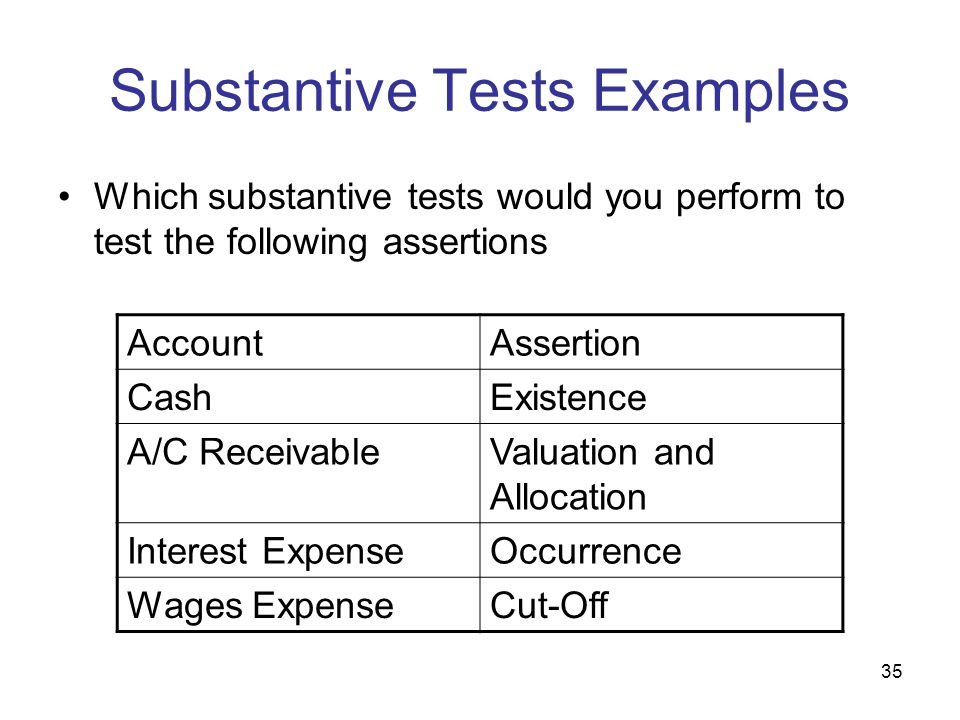
Substantive Procedures in Auditing: Definition & Explanation
They might even select a sample of products and physically count the products to ensure the inventory ledger agrees with the actual physical count. This would be a procedure to test the valuation assertion. If the financial statements say that a company has $500,000 in the bank, the auditors want evidence that there is actually $500,000 in the bank. First, they obtain the final version of the balance sheet and look at the amount of cash the company reports. Second, they research the cash ledger and identify where that cash is located.
Int Ctrl tests have to do with finding an error in processesing data. Whereas, $ubstantive testing has to do with dollar amounts.
Account reconciliations are substantive procedures that require the auditor to trace the components of one account to some source documentation. For example, let’s consider a kiosk in the mall that sells smartphone cases. They might report on their financial statements that they have $30,000 in inventory. To confirm that, the auditor would look at the inventory records and ensure that the value of each item was accurate and that the quantity and value of all the different products added up to $30,000.
Another substantive procedure performed by auditors is document matching. This is simply obtaining two documents from two different, independent sources and making sure they match, or agree, with one another. This is a common procedure for auditing accounts receivable (A/R).
What is test of control and substantive test?
Substantive testing is an audit procedure that examines the financial statements and supporting documentation to see if they contain errors. These tests are needed as evidence to support the assertion that the financial records of an entity are complete, valid, and accurate.
An accounts receivable balance means the company is saying that customers owe them money. To test for that, the auditor would look at the A/R ledger and select a customer account. They would look at the balance for that account, and then find the customer’s order and company’s invoice.
B) The systems approach focuses on detailed testing of specific accounts for accuracy, while the substantive approach is the testing controls to make sure they are effective. C) The systems approach focuses on the use of computer systems to aid in the audit while the substantive approach focuses on more manual tests. D) A thoroughly designed systems approach to auditing can eliminate the need for any substantive procedures. Substantive procedures are used during an audit to test for a material misstatement of the financial statements. Substantive procedures (or substantive tests) are those activities performed by the auditor to detect material misstatement or fraud at the assertion level.
If sufficient appropriate audit evidence cannot be obtained, or the evidence points to a material misstatement in the FS, the auditor will have to issue a modified audit opinion. Auditing is a profession that lives by the adage ‘Trust, but verify.’ Auditors verify by performing substantive tests to obtain documented evidence that supports some assessment or conclusion about some aspect of an organization. Examples of common substantive procedures that auditors routinely perform are bank confirmations, account reconciliations, and document matching.
The final step is simply counting the cash in the petty cash safe and then calling the bank to get account statements for the date of the financial reports. If the bank statement reports the same amount as the cash ledger, then the conclusion is that the cash account is complete and correct. The auditor saves the copies of the bank statements, the cash ledger, the financial statements, and their cash count sheet as evidence of their conclusion.
Most of the work auditors do is aimed at conducting substantive procedures. If you’ve ever worked at an organization that has been audited by external or internal auditors, you likely remember the requests for documentation, reports, and other original information. reduce the level of substantive procedures; by relying on the entity’s internal controls, but auditor must test those controls; and determine whether or not the internal controls are actually effective. There are two main types of activities auditors perform–tests of internal controls and $ubstantive testing.
You must create an account to continue watching
To qualify as a substantive procedure, enough documentation must be collected so that another competent auditor could conduct the same procedure on the same documents and make the same conclusion. Analytical procedures include comparison of financial information (data in financial statement) with prior periods, budgets, forecasts, similar industries and so on. It also includes consideration of predictable relationships, such as gross profit to sales, payroll costs to employees, and financial information and non-financial information, for examples the CEO’s reports and the industry news. Analytical procedures are an important part of the audit process and consist of evaluations of financial information made by a study of plausible relationships among both financial and nonfinancial data.
Tour the client’s facilities and review the general records. Consult with and review the work of the predecessor auditors prior to discussing the engagement with the client management. Which of the following statements is not correct regarding the auditor’s determination of materiality? It is the smallest amount of misstatement that would probably influence the judgment of a reasonable person relying upon the financial statements.
Analytical procedures range from simple comparisons to the use of complex models involving many relationships and elements of data. A basic premise underlying the application of analytical procedures is that plausible relationships among data may reasonably be expected to exist and continue in the absence of known conditions to the contrary. Particular conditions that can cause variations in these relationships include, for example, specific unusual transactions or events, accounting changes, business changes, random fluctuations, or misstatements. The purpose of audit tests, or audit procedures, is to allow the auditor to collect sufficient appropriate audit evidence to be able to conclude with reasonable assurance that the financial statements (FS) are free of material misstatement.
- The auditor considers the level of assurance, if any, he wants from substantive testing for a particular audit objective and decides, among other things, which procedure, or combination of procedures, can provide that level of assurance.
- For other assertions, however, analytical procedures may not be as effective or efficient as tests of details in providing the desired level of assurance.
What are the substantive procedures in auditing?
Test of controls is an audit test to test the effectiveness of the client’s internal control system. substantive procedures is an audit test to test the reasonableness of items in the finincial statements. If the internal control is effective, then the auditor will use more test of controls and less substantive tests.

Analytical procedures involve comparisons of different sets of financial and operational information, to see if historical relationships are continuing forward into the period under review. In most cases, these relationships should remain consistent over time. If not, it can imply that the client’s financial records are incorrect, possibly due to errors or fraudulent reporting activity. If the auditor is unable to obtain a letter containing management assertions from the senior management of a client, the auditor is unlikely to proceed with audit activities. One reason for not proceeding with an audit is that the inability to obtain a management assertions letter could be an indicator that management has engaged in fraud in producing the financial statements.
Analytical procedures are a type of evidence used during an audit. These procedures can indicate possible problems with the financial records of a client, which can then be investigated more thoroughly.
Which of the following is the most likely first step the auditors would perform at the beginning of an initial audit engagement? Prepare a rough draft of the financial statements and of the auditors’ report.
Which of the following is most likely to be an overall response to fraud risks identified in an audit? Decrease the use of professional skepticism and increase the use of internally generated evidence. Consider further management’s selection and application of significant accounting principles. Supervise members of the audit team less closely and rely more upon judgment. Which of the following is least likely to be considered a risk assessment procedure in a financial statement audit?
AccountingTools
Those are two different documents from two different sources that should match. If they do, they can then look for payments made by the customer. After accounting for any payments, the balance should be the same as reported in the A/R ledger. A substantive procedure is a process, step, or test that creates conclusive evidence regarding the completeness, existence, disclosure, rights, or valuation (the five audit assertions) of assets and/or accounts on the financial statements.
For other assertions, however, analytical procedures may not be as effective or efficient as tests of details in providing the desired level of assurance. When designing substantive analytical procedures, the auditor also should evaluate the risk of management override of controls. As part of this process, the auditor should evaluate whether such an override might have allowed adjustments outside of the normal period-end financial reporting process to have been made to the financial statements. Such adjustments might have resulted in artificial changes to the financial statement relationships being analyzed, causing the auditor to draw erroneous conclusions. For this reason, substantive analytical procedures alone are not well suited to detecting fraud.
Auditing standards require auditors to consider materiality in planning the audit. The planning level of materiality will normally be the larger of the amount considered for the balance sheet versus the income statement. The appropriate financial statement base for computing materiality may vary based on the nature of the client’s business. Which statement best describes the interaction of the systems and substantive approaches in the audit plan? A) The systems approach focuses on testing controls to make sure they are effective, while the substantive approach is the detailed testing of specific accounts for accuracy.
Transferring credit to the school of your choice
Analytical procedures may be effective and efficient tests for assertions in which potential misstatements would not be apparent from an examination of the detailed evidence or in which detailed evidence is not readily available. For example, comparisons of aggregate salaries paid with the number of personnel may indicate unauthorized payments that may not be apparent from testing individual transactions. Differences from expected relationships may also indicate potential omissions when independent evidence that an individual transaction should have been recorded may not be readily available. When the evidence obtained from analytical procedures and test of details of related balance accounts does not reduce detection risk to an acceptably low level, direct tests of details of assertions about income statement accounts are necessary. For our company with $500,000, the cash ledger may report that $5,000 is kept onsite for petty cash and customer receipts, $245,000 is kept at ABC Bank in a checking account, and $250,000 is kept at XYZ Bank in a savings account.
The auditor considers the level of assurance, if any, he wants from substantive testing for a particular audit objective and decides, among other things, which procedure, or combination of procedures, can provide that level of assurance. For some assertions, analytical procedures are effective in providing the appropriate level of assurance.