Should I have a savings as well as salary account?
Outstanding Salary A/c is a Representative Personal Account as it represents a group of people to whom some amount of salary is payable. Similarly other outstanding and prepaid expenses also fall under the category of representative personal accounts. For tax purposes, the Internal Revenue Code permits the deduction of business expenses in the tax payable year in which those expenses are paid or incurred.
Salaries payable
The cost of purchasing gas does not improve or prolong the life of the truck but simply allows the truck to run. Salaries Expense will usually be an operating expense (as opposed to a nonoperating expense). Depending on the function performed by the salaried employee, Salaries Expense could be classified as an administrative expense or as a selling expense. If the employee was part of the manufacturing process, the salary would end up being part of the cost of the products that were manufactured.
Liabilities and stockholders’ equity, to the right of the equal sign, increase on the right or CREDIT side. Gross profit is the profit a company makes after deducting the costs associated with making and selling its products, or the costs associated with providing its services. Gross profit will appear on a company’s income statement and can be calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from revenue (sales).
(The costs of the products that are not sold are reported as inventory on the balance sheet. Hence, the inventory will contain some of the manufacturing salaries and wages. The accrued salaries entry is a debit to the compensation (or salaries) expense account, and a credit to the accrued wages (or salaries) account. The accrued wages account is a liability account, and so appears in the balance sheet.
Revenue represents the total income of a company before deducting expenses. Companies looking to increase profits want to increase their receivables by selling their goods or services. Typically, companies practice accrual-based accounting, wherein they add the balance of accounts receivable to total revenue when building the balance sheet, even if the cash hasn’t been collected yet. In double-entry bookkeeping, expenses are recorded as a debit to an expense account (an income statement account) and a credit to either an asset account or a liability account, which are balance sheet accounts.
Accounting treatment of salary payable:
For example, the terms could stipulate that payment is due to the supplier in 30 days or 90 days. The payable is in default if the company does not pay the payable within the terms outlined by the supplier or creditor. Recording transactions into journal entries is easier when you focus on the equal sign in the accounting equation. Assets, which are on the left of the equal sign, increase on the left side or DEBIT side.
What are salaries payable?
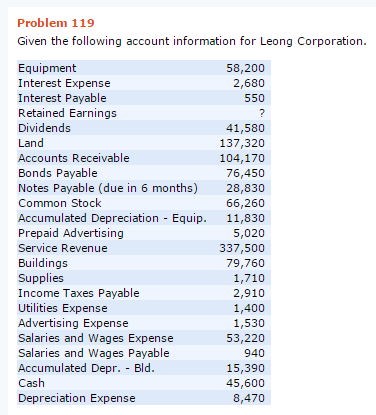
Salaries payable is a liability account that contains the amounts of any salaries owed to employees, which have not yet been paid to them. The balance in the account represents the salaries liability of a business as of the balance sheet date.
So, Unpaid salary to be shown as liability under ‘Expenses Payable’ or ‘Salary Payable’ in Balance sheet on liabilities side and on other aspect of dual entry to be placed in Profit & Loss Account. Revenue is only increased when receivables are converted into cash inflows through the collection.
- So, Unpaid salary to be shown as liability under ‘Expenses Payable’ or ‘Salary Payable’ in Balance sheet on liabilities side and on other aspect of dual entry to be placed in Profit & Loss Account.
- Revenue represents the total income of a company before deducting expenses.
This is in contrast to capital expenditures that are paid or incurred to acquire an asset. Expenses are costs that do not acquire, improve, or prolong the life of an asset. For example, a person who buys a new truck for a business would be making a capital expenditure because they have acquired a new business-related asset. However, the gas the person buys during that year to fuel that truck would be considered a deductible expense.
Salary Payable Definition
Salary payable is classified as a current liability account that appears under the head of current liabilities on the balance sheet. All the general rules of accounting are also applicable to this account. Companies must maintain the timeliness and accuracy of their accounts payable process. Delayed accounts payable recording can under-represent the total liabilities. This has the effect of overstating net income in financial statements.
It is usually included in the current liabilities on the balance sheet as it is expected to be paid within one year. The column order on the spreadsheet is date, description, debit and credit. Enter the gross payroll amount (salary expense) in the debit (left) column. Starting on the next line, on one line each, enter a payable account in the description column and the amount deducted from your employee’s pay in the credit (right) column.
Accounts payable is a liability since it’s money owed to creditors and is listed under current liabilities on the balance sheet. Current liabilities are short-term liabilities of a company, typically less than 90 days. Salary payable can be attributed to the type of payroll journal entry that shall be used to record in the books of account the compensation which shall be paid to the employees.
Effective and efficient treatment of accounts payable impacts a company’s cash flow, credit rating, borrowing costs, and attractiveness to investors. To see how accounts payable is listed on the balance sheet, below is an example of Apple Inc.’s balance sheet, as of the end of their fiscal year for 2017, from their annual 10K statement.

Payroll accruals are sums that your business owes to workers for hours they have worked. Because few companies pay employees immediately, there is usually a lag time between the end of a pay period and the date you compensate employees for their time. This information is relevant when you create a balance sheet because it represents an amount that your company does not actually own, although you may have the money in the bank.
Typical business expenses include salaries, utilities, depreciation of capital assets, and interest expense for loans. The purchase of a capital asset such as a building or equipment is not an expense.
Unpaid salaries are salary liabilities that you have incurred but have not paid. You must record all accrued salaries, employment taxes and related compensation expenses in the same period in which they are incurred. If there is a gap between the date of the last payroll deposit and the date on which you prepare the financial statements, make an adjusting journal entry to record the incurred salary expense. A company’s journal contains a chronological record of financial transactions.
Payroll accruals are also important for internal accounting because they help your company to determine how much you spent on payroll during any given month. At a manufacturing company, the salaries and wages of employees in the manufacturing operations are assigned to the products manufactured. When the products are sold, the costs assigned to those products (including the manufacturing salaries and wages) are included in the cost of goods sold, which is reported on the income statement.