Sales revenue definition
Revenue is the money a company earns from the sale of its products and services. Cash flow is the net amount of cash being transferred into and out of a company.
Revenue provides a measure of the effectiveness of a company’s sales and marketing, whereas cash flow is more of a liquidityindicator. Both revenue and cash flow are used to help investors andanalysts evaluate the financial health of a company.
We can see that the cash flow statement shows the debits and credits to the cash position of the company. However, revenue is the money earned from sales and other various income-producing activities. Revenue is often referred to as thetop linebecause it sits at the top of theincome statement. Revenue represents the total income earned by a companybeforeexpenses are deducted.
Also, there may be production-related expenses (such as facility rent) even when there is no production at all, as would be the case when there is a union walkout. In these cases, it is possible for there to be a cost of goods sold expense even in the absence of sales.
Businesses that might have no cost of goods sold include attorneys, painters, business consultants, and doctors. Although the cost of revenue factors in many costs associated with sales, it does not take into account the indirect costs, such as salaries paid to managers. The costs considered part of the cost of revenue include a multitude of items, such as the cost of labor, commission, materials, and sales discounts. Gross profit is revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS), which are the direct costs attributable to the production of the goods sold in a company.
Cost of Revenue vs. Cost of Goods Sold
This line item is the aggregate amount of expenses incurred to create products or services that have been sold. The cost of goods sold is considered to be linked to sales under the matching principle. Thus, once you recognize revenues when a sale occurs, you must recognize the cost of goods sold at the same time, as the primary offsetting expense. It appears in the income statement, immediately after the sales line items and before the selling and administrative line items.
Cash flow is reported on the cash flow statement (CFS), which shows the sources of cash as well as how cash is being spent. The top line of the cash flow statement begins with net income or profit for the period, which is carried over from the income statement. If you recall, revenue sits at the top of the income statement, and after all expenses and costs are subtracted, net income is the result and sits at the bottom of the income statement.
For example, revenue drivers for an outpatient clinic include the number of people receiving services, the type of services delivered, and the amount charged for delivering services. Cost drivers for the clinic include staff/labor costs, administrative costs, and facility costs. The cost of revenue is the total cost of manufacturing and delivering a product or service and is found in a company’s income statement. Companies that offer both services and goods are likely to have both the cost of goods sold, and the cost of sales appear on their income statements.
The cost of revenue is the total cost of manufacturing and delivering a product or service to consumers. Cost of revenue information is found in a company’s income statement and is designed to represent the direct costs associated with the goods and services the company provides. The service industry often favors using the cost of revenue metric because it is a more comprehensive account of the various costs associated with selling a good or service. The cost of sales and COGS are key metrics in cost analysis since they show the operational costs of the production of goods and services.
Cost of sales, also known as the cost of revenue, and cost of goods sold (COGS), both keep track of how much it costs a business to produce a good or service to be sold to customers. Both the cost of sales and COGS include the direct costs associated with the production of a company’s goods and services. These costs include direct labor, direct materials, such as raw materials, and the overhead that’s directly tied to the production facility or manufacturing plant. This is because it includes the COGS or cost of services and other direct costs.
How operating expenses and cost of goods sold differ?
The contribution margin includes total variable costs, and the gross margin only includes the COGS or the cost of services. A company with a low cost of revenue to total revenue percentage indicates that it is in stable financial health and may have strong sales. Retailers typically use the cost of sales, whereas manufacturers use the cost of goods sold. Since service-only businesses cannot directly tie any operating expenses to something tangible, they cannot list any cost of goods sold on their income statements. Instead, service-only companies typically show the cost of sales or cost of revenue.
The company had direct labor costs of $5 million, marketing expenses of $1 million, and direct overhead costs of $3 million. Additionally, the company paid $10 million to its management and had rental costs of $8 million.
- Both the cost of sales and COGS include the direct costs associated with the production of a company’s goods and services.
- These costs include direct labor, direct materials, such as raw materials, and the overhead that’s directly tied to the production facility or manufacturing plant.
- Cost of sales, also known as the cost of revenue, and cost of goods sold (COGS), both keep track of how much it costs a business to produce a good or service to be sold to customers.
Effective strategic plans include key financial metrics to monitor organizational activities on a real-time basis. Financial metrics are developed by identifying the revenue and cost drivers of each business unit or activity.
Examples of Industries That Cannot Claim Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
This amount includes the cost of the materials used in creating the good along with the direct labor costs used to produce the good. Revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods or services related to the company’s primary operations. Profit, typically called net profitor the bottom line, is the amount of income that remains after accounting for all expenses, debts, additional income streams and operating costs. The cost of goods sold is usually the largest expense that a business incurs.
There are different ways to calculate revenue, depending on the accounting method employed. Accrual accounting will include sales made on credit as revenue for goods or services delivered to the customer. It is necessary to check the cash flow statement to assess how efficiently a company collects money owed.Cash accounting, on the other hand, will only count sales as revenue when payment is received. For example, if the customer paid in advance for a service not yet rendered or undelivered goods, this activity leads to a receipt but not revenue.
What is the Cost of Revenue?
The process of organizing revenue and costs and assessing profit typically falls to accountants in the preparation of a company’s income statement. One step further, subtracting fixed costs, gets you operating profit. Once irregular revenue and expenses are added, you get bottom-line net profit. Assume XYZ Inc. sells electronics products and offers services to repair electronic equipment. XYZ Inc. reported total revenue of $100 million, COGS of $15 million, and cost of services sold of $7 million.
What is difference between cost and revenue?
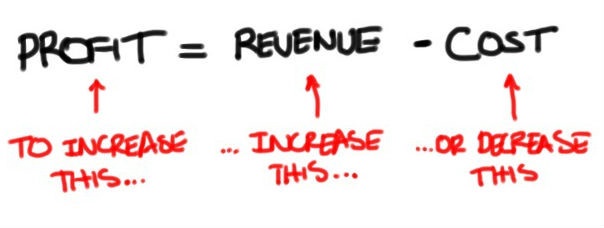
The difference between the revenue and cost (found by subtracting the cost from the revenue) is called the profitThe difference between revenue and cost when revenue exceeds the cost incurred in operating the business The revenue would be $1.50 per ice cream bar times 36,000 ice cream bars, or $54,000.
The locations are why revenue is often called the top-line number, while net income or profit is called the bottom line number. Revenue can be broken down and listed as separate line items on a company’s income statement based on the type of revenue. For example, many companies list operating income separately, which is the money earned from a company’s core business operations.
If the cost of sales is rising while revenue has stagnated, it might be an indication that input costs have increased or other direct costs are not being appropriately managed. Cost of sales and COGS are subtracted from total revenue to yield gross profit. The Income Statement is one of a company’s core financial statements that shows their profit and loss over a period of time. If there are no sales of goods or services, then there should theoretically be no cost of goods sold. Instead, the costs associated with goods and services are recorded in the inventory asset account, which appears in the balance sheet as a current asset.
Cost of Revenue vs Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
What is included in cost of revenue?
Cost of Revenues refers to the directly attributable to the goods or services of a company and includes the manufacturing, production and distribution cost of a product or service to its customers.
Conversely, non-operating revenue is the money earned from secondary sources, which could be investment income or proceeds from the sale of an asset. Other costs included in the cost of revenue are the cost of labor to sell a service and the cost of making sales calls. The cost of revenue, on the other hand, is more general and includes the cost of goods sold as well as a range of other costs to make a sale possible. Operating income is an accounting figure that measures the amount of profit realized from a business’s operations, after deducting operating expenses such as wages, depreciation, and cost of goods sold (COGS). Revenue is known as the top line because it appears first on a company’s income statement.