How to Calculate Job Costing
Process cost procedures
Costs are likely to be accumulated at the department level, and no lower within the organization. Process costing is a type of operation costing which is used to ascertain the cost of a product at each process or stage of manufacture.
Analyzing trends on costs of production and overhead along with revenue helps management make informed decisions on how to improve, scale, or grow effectively. Cost accounting utilizes either job costing, process costing, or a hybrid of both.
Unit Cost Information Similarities Unit cost information is needed by management for decision-making purposes. Differences Process Costing Job Costing Unit cost information comes from the departmental production cost report. Inventory Accounts Similarities Inventory accounts include raw materials inventory, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods inventory.
To determine the cost per unit under process costing, each expense must first be assigned to a process then categorized as a direct materials cost or conversion cost. Once these steps have been completed, the expenses can be divided by total units produced to obtain the cost per unit.
In this article, we will discuss the differences between job costing and process costing as well as advantages or disadvantages of each. Direct materials are materials that are consumed during the manufacture of a product.
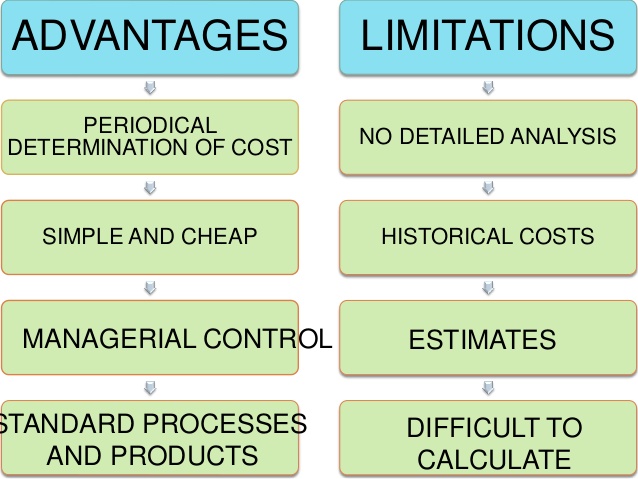
Process costing is suitable for industries producing homogeneous products and where production is a continuous flow. A process can be referred to as the sub-unit of an organization specifically defined for cost collection purpose. Why have three different cost calculation methods for process costing, and why use one version instead of another? The different calculations are required for different cost accounting needs.

In other words, the cost of each product produced is assumed to be the same as the cost of every other product. Under this concept, costs are accumulated over a fixed period of time, summarized, and then allocated to all of the units produced during that period of time on a consistent basis. When products are instead being manufactured on an individual basis, job costing is used to accumulate costs and assign the costs to products. When a production process contains some mass manufacturing and some customized elements, then a hybrid costing system is used.
- Product Costs Similarities Product costs consist of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Process Costing
What is an example of process costing?
Process costing is a method of costing used mainly in manufacturing where units are continuously mass-produced through one or more processes. Examples of this include the manufacture of erasers, chemicals or processed food.
Differences Process Costing Job Costing Several different work-in-process inventory accounts are used—one for each department (or process). One work-in-process inventory account is used—job cost sheets track costs assigned to each job. Cost accounting helps managers determine the costs of running a business by recording the costs of materials, processes, and projects.
A hybrid cost accounting system is one that includes parts of job costing and process costing. When a business creates or manages products in batches and charges based on the batch as well as costs labor as an individual unit, hybrid costing can help. Prefabrication contractors are an example of those who benefit from hybrid costing. Each unit prefabricated for a project, or batch, is cost based on the batch. While the workers are usually cost based on the hours worked on an individual unit level.
What is process costing?
Recall the three components of product costs—direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Assigning these product costs to individual products remains an important goal for process costing, just as with job costing. However, instead of assigning product costs to individual jobs (shown on a job cost sheet), process costing assigns these costs to departments (shown on a departmental production cost report). Process costing is used when there is mass production of similar products, where the costs associated with individual units of output cannot be differentiated from each other.
The first department in the process is the casting department, where the widgets are initially created. During the month of March, the casting department incurs $50,000 of direct material costs and $120,000 of conversion costs (comprised of direct labor and factory overhead). The widgets then move to the trimming department for further work, and these per-unit costs will be carried along with the widgets into that department, where additional costs will be added. In accounting, process costing is a method of assigning production costs to units of output. In process costing systems, production costs are not traced to individual units of output.
Product Costs Similarities Product costs consist of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Differences Process Costing Job Costing Product costs are assigned to departments (or processes).
Join PRO or PRO Plus and Get Lifetime Access to Our Premium Materials
This can ensure that the overall rice is still low enough to remain competitive while covering all operational, material and labor costs. Process costing is straightforward to track versus the detailed record keeping in job costing. Each department tracks their material and labor costs as the product moves through their department. Accountants divide costs by the number of units to total an average production cost. As a process costing example, ABC International produces purple widgets, which require processing through multiple production departments.
However, job costing does not work for manufacturing companies that produce products that are identical, or very similar, such as food or oil, because each unit costs the same to produce. Process costing systems allocate expenses to products by adding total costs at each stage of the manufacturing process then dividing these costs by the total number of units produced. This enables these companies to determine the costs associated with the products at each stage of the manufacturing process and cut costs as necessary per stage of manufacture. Process costing involves the accumulation of costs for lengthy production runs involving products that are indistinguishable from each other.
Then assign the costs to units of output as they move through the departments. The process costing method is typically used for processes that produce large quantities of homogeneous products.