How Dos a Business Use a Profit and Loss Statement?
Who Uses an Income Statement?
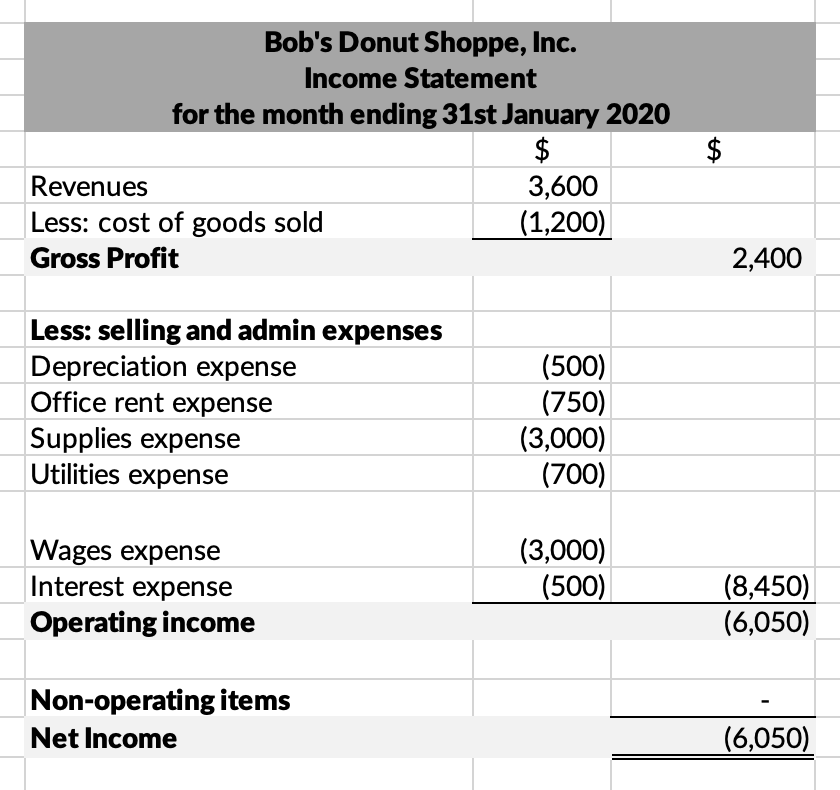
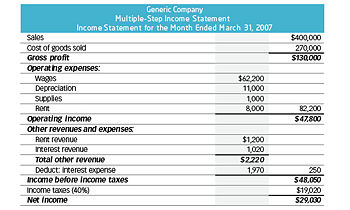
Essentially, the different measures of profitability in a multiple-step income statement are reported at four different levels in a business’ operations – gross, operating, pre-tax and after-tax. As we shall shortly see in the following example, this segregation helps in identifying how the income and profitability are moving/changing from one level to the other. For instance, high gross profit but lower operating income indicates higher expenses, while higher pre-tax profit and lower post-tax profit indicates loss of earnings to taxes and other one-time, unusual expenses. The income statement tells you how much money a company has brought in (its revenues), how much it has spent (its expenses), and the difference between the two (its profit). The income statement shows a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific time frame such as three months or a year.
How do you make an income statement?
The income statement calculates the net income of a company by subtracting total expenses from total income. For example annual statements use revenues and expenses over a 12-month period, while quarterly statements focus on revenues and expenses incurred during a 3-month period.
This can provide a useful comparison to the income statement, especially when the amount of profit or loss reported does not reflect the cash flows experienced by the business. This statement may be presented when issuing financial statements to outside parties. The header identifies the company, the statement and the period to which the statement relates, the reporting currency and the level of rounding-off.
In case of a consolidated income statement, a distribution of net income between the equity-holders of the parent and non-controlling interest holders is also presented. The statement normally ends with a presentation of earnings per share, both basic and diluted. Important line items such as revenue, cost of sales, etc. are cross-referred to the relevant detailed schedules and notes. The financial statements of a company provide a representation of the company’s current performance to investors.
Components of an Income Statement
This information is then used to determine the total profit or loss to the company over the stated accounting period. The Income Statement is one of a company’s core financial statements that shows their profit and loss over a period of time. Note by the way, that reports of “Income,” “Revenues,” and “Expenses” do not necessarily represent real cash inflows or outflows. Not all of these signal the presence of “cash flow” for the following reason.
This statement contains the information you’ll most often see mentioned in the press or in financial reports–figures such as total revenue, net income, or earnings per share. Presents the revenues, expenses, and profits/losses generated during the reporting period. This is usually considered the most important of the financial statements, since it presents the operating results of an entity. The income statement, also called theprofit and loss statement, is a report that shows the income, expenses, and resulting profits or losses of a company during a specific time period.
ottom line Net income is one measure of the company’s financial performance for the period. However, the Income statement contains other performance metrics as well. The difference between Net sales revenues and Cost of goods sold is called Gross profit, for instance. And, net income from operations—before taxes, before gains and losses from financial and extraordinary items—is named, not surprisingly, Operating Income or operating profit. Income statements show how much profit a business generated during a specific reporting period and the amount of expenses incurred while earning revenue.
Creditors may find limited use of income statements as they are more concerned about a company’s future cash flows, instead of its past profitability. Research analysts use the income statement to compare year-on-year and quarter-on-quarter performance. One can infer whether a company’s efforts in reducing the cost of sales helped it improve profits over time, or whether the management managed to keep a tab on operating expenses without compromising on profitability. Presents the cash inflows and outflows that occurred during the reporting period.
This information is used to evaluate the overall value of a company and its share price. The income statement is one of the most important financial statements because of its indication of profits, its timely reporting, and its classification of revenues and expenses.
- Also known as the profit and loss statement or the statement of revenue and expense, the income statement primarily focuses on the company’s revenues and expenses during a particular period.
What is income statement with example?
The Income Statement is one of a company’s core financial statements that shows their profit and loss. The P&L statement shows a company’s ability to generate sales, manage expenses, and create profits. over a period of time.
Also known as the profit and loss statement or the statement of revenue and expense, the income statement primarily focuses on the company’s revenues and expenses during a particular period. The income statement is one the major financial statements used to analyze a company.
Income Statement Template
International Accounting Standard 7 (IAS 7) is the International Accounting Standard that deals with cash flow statements. The income statement is one of the financial statements of an entity that reports three main financial information of an entity for a specific period of time.
The header is followed by revenue and cost of goods sold and calculation of gross profit. Further down the statement there is detail of operating expenses, non-operating expenses, and taxes and eventually the statement presents net income differentiating between income earned from continuing operations and total net income.
The other important documents are the balance sheet, the cash flow statement and the statement of shareholder’s equity. The income statement is used to give a summary of the company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period of time.
What are Common Drivers for Each Income Statement Item?
A profit and loss statement (P&L), or income statement or statement of operations, is a financial report that provides a summary of a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits/losses over a given period of time. The P&L statement shows a company’s ability to generate sales, manage expenses, and create profits.
Regulatory groups, standards boards, and tax authorities allow or require companies to use conventions such as depreciation expense, cost allocation, and accrual accounting on the Income statement. Direct reports of actual cash flow gains and losses for the period appear on another reporting instrument, the Statement of changes in financial position (or Cash flow statement). An income statement is one of the three (along with balance sheet and statement of cash flows) major financial statements that reports a company’s financial performance over a specific accounting period. Essentially, the cash flow statement is concerned with the flow of cash in and out of the business. As an analytical tool, the statement of cash flows is useful in determining the short-term viability of a company, particularly its ability to pay bills.
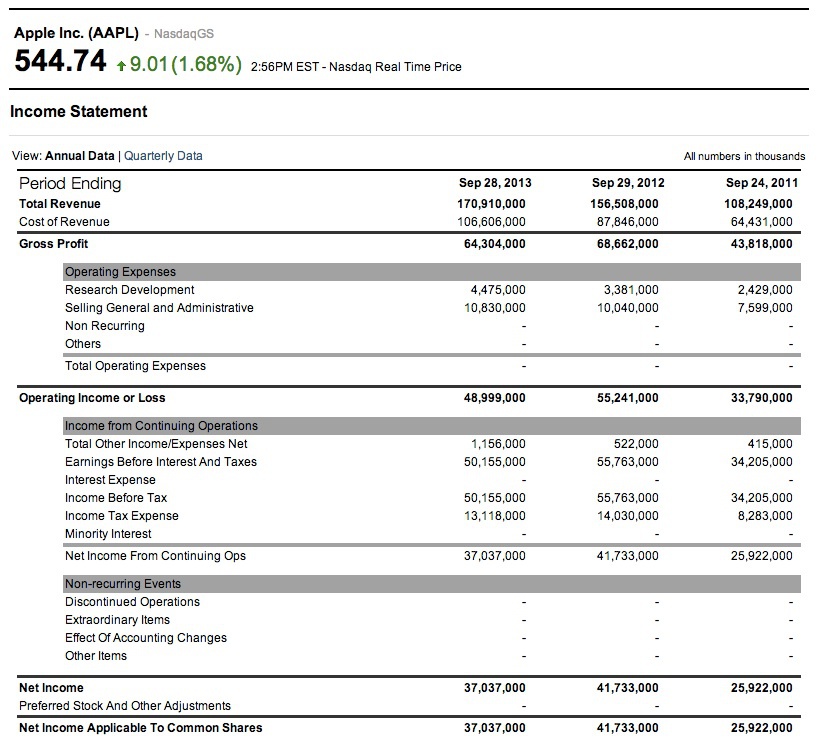
Those information included revenues, expenses, and profit or loss for the period of time. Although this brochure discusses each financial statement separately, keep in mind that they are all related. The changes in assets and liabilities that you see on the balance sheet are also reflected in the revenues and expenses that you see on the income statement, which result in the company’s gains or losses. Cash flows provide more information about cash assets listed on a balance sheet and are related, but not equivalent, to net income shown on the income statement. And information is the investor’s best tool when it comes to investing wisely.