Earned Income Is Taxed Differently Than Unearned Income
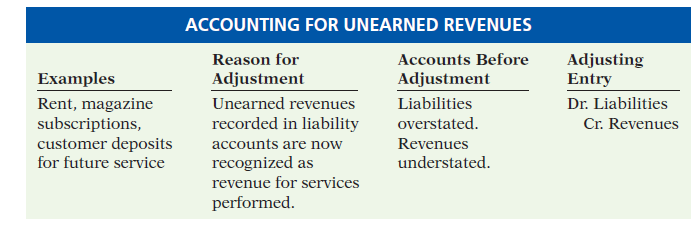
Typically, a business does not recognize payments from unearned revenue accounts all at once. To do so would overstate the company’s actual revenues and profits during a specific period. Conversely, revenues and profits would be understated in following periods when revenues went unrecognized but expenses related to providing goods and services were recognized. Businesses sometimes need to make an unearned revenue adjusting entry to their balance sheet. These entries reflect goods and services that the company has been paid for but not yet provided.
In addition, any pre-tax salary deferral contribution made to a retirement account, pension plan, or another pre-tax account will reduce your federal and state income tax liability in the contribution year. Unearned revenue is money received from a customer for work that has not yet been performed. This is advantageous from a cash flow perspective for the seller, who now has the cash to perform the required services. Unearned revenue is a liability for the recipient of the payment, so the initial entry is a debit to the cash account and a credit to the unearned revenue account. When the transaction occurs, such as a publishing company selling a magazine subscription, the journal entry includes a debit to cash and a credit to unearned revenue.
Unearned revenue is an important concept in accounting because the company cannot recognize the revenue until it provides the good or service to the customer who paid for it. The line item “Unearned Revenue” or “Deferred Income” gives the company a place to recognize that the cash payment has come in but the company has deferred the revenue recognition until a later date. If you are at an early stage in your career, maximize earned income sources to qualify for contribution to retirement accounts and grow your nest egg with the help of compounding returns. Because payroll taxes will get taken out of earned income, also aim to secure at least a few sources of unearned income, which will be exempt from payroll taxes.

In such cases, the unearned revenue will appear as a long-term liability on the balance sheet. If a publishing company accepts $1,200 for a one-year subscription, the amount is recorded as an increase in cash and an increase in unearned revenue. Both are balance sheet accounts, so the transaction does not immediately affect the income statement. If it is a monthly publication, as each periodical is delivered, the liability or unearned revenue is reduced by $100 ($1,200 divided by 12 months) while revenue is increased by the same amount.

As the prepaid service or product is gradually delivered over time, it is recognized as revenue on theincome statement. It is a liability because even though a company has received payment from the customer, the money is potentially refundable and thus not yet recognized as revenue. Because of the nature of how the revenue is documented in journals, it is sometimes referred to as an unearned income journal entry. However, the nature of documenting and changing these entries remains the same. As the service or goods are provided, businesses debit the total unearned revenue entry and credit the earned revenue entry to reflect the change.
When this right is purchased, the gym would get the cash for a year of service it has yet to provide. So when the cash is originally received, it will be recorded as unearned revenue. As each month passes a portion of that unearned revenue will be reclassified as “earned,” given that the service, a month of gym usage, will be provided. Unearned revenue that will be earned within the year and thus “pay off” the liability, is a current liability. DebitCreditCash10,000Accounts Receivable25,000Interest Receivable600Supplies1,500Prepaid Insurance2,200Trucks40,000Accum.
Unearned Revenue
The income statement, or statement of earnings, does not reflect that the company has made a sale until it has earned the income by delivering the magazines to the customer. In accounting terms, unearned revenue forms a debit, or loss, to the recipient. Unearned revenue is accounted for on a business’ balance sheet as an existing, current liability. Current liabilities represent obligations that the business has yet to meet.
- It is classified as current liability and is shown in current liabilities section of the balance sheet.
- Unearned revenuearises when payment is received from customers before the services are rendered or goods are delivered to them.
- According to revenue recognition principle of accounting, the unearned revenue is not treated as revenue until the related goods and/or services are provided to customers.
Accounting for Unearned Revenue
On January 15, 2019, when the Mexico Company will deliver goods to New York Company, it will eliminate the unearned revenue liability and recognize revenue in its accounting records. This revenue will be reported in the income statement that will be prepared by the mexico company on December 31, 2019. This is money paid to a business in advance, before it actually provides goods or services to a client.
As you approach retirement, make the transition to less earned income and more unearned income. This approach will benefit you as a retiree, when your goal will be to minimize taxes and draw a sustainable income.
Unearned revenue is recorded on a company’s balance sheet as a liability. It is treated as a liability because the revenue has still not been earned and represents products or services owed to a customer.
Accounting reporting principles state that unearned revenue is a liability for a company that has received payment (thus creating a liability) but which has not yet completed work or delivered goods. The rationale behind this is that despite the company receiving payment from a customer, it still owes the delivery of a product or service. If the company fails to deliver the promised product or service or a customer cancels the order, the company will owe the money paid by the customer. Unearned revenue is usually disclosed as a current liability on a company’s balance sheet. This changes if advance payments are made for services or goods due to be provided 12 months or more after the payment date.
What is unearned revenue example?
Unearned revenue is money received by an individual or company for a service or product that has yet to be provided or delivered. It can be thought of as a “prepayment” for goods or services that a person or company is expected to supply to the purchaser at a later date.
Unearned revenue is cash received by a business for goods or services yet to be provided. It is recorded as a liability on the business’s balance sheet until the contract is completed. Unearned revenue can be accrued in a variety of different ways.
Deferred Revenue vs. Accrued Expense: What’s the Difference?
When the goods or services are provided, an adjusting entry is made. Unearned revenue is helpful to cash flow, according to Accounting Coach. Unearned revenue occurs when a company sells a good or service in advance of the customer receiving it. Customers often receive discounts for paying in advance for goods or services.
Example of Unearned Revenue
For example, Mexico Manufacturing Company receives $25,000 cash from New York Trading Company on December 1, 2018. According to agreement, the Mexico Company will manufacture and provide goods to New York Company on January 15, 2019 against the payment received on December 31, 2018. The amount of $25,000 will remain an unearned revenue for Mexico Company until it manufactures and delivers goods to New York Company on January 15, 2019. If Mexico Company prepares its annual financial statements on December 31, 2018, it must report this unearned revenue of $25,000 in current liabilities section of its balance sheet.
Unearned revenuearises when payment is received from customers before the services are rendered or goods are delivered to them. According to revenue recognition principle of accounting, the unearned revenue is not treated as revenue until the related goods and/or services are provided to customers. It is classified as current liability and is shown in current liabilities section of the balance sheet.
The balance sheet is adjusted as the business provides the purchased goods or services, resulting in a reduction of currently existing liabilities. This is reflected on the balance sheet as a debit to the unearned revenue account and a credit to the balance of the revenue account.