Difference Between Report Form and Account Form Balance Sheets
Gross profit less the monthly expenses leaves net income as the income statement’s final number. The income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement are the three most common financial statements. Business owners use each statement to analyze various pieces of their company’s financial information. Smaller or home-based businesses using cash basis accounting methods will not have a cash flow statement. Cash flow statements are only used by companies using the accrual accounting method.
Sales revenue is first, cost of goods sold second and expenses third on the financial statement. Sales revenue less cost of goods sold is the company’s gross profit.
The balance sheet
It shows you how much you made (revenue) and how much you spent (expenses). Personal financial statements are most often used when an individual is applying for credit, such as loans or a mortgage.
The changes in assets and liabilities that you see on the balance sheet are also reflected in the revenues and expenses that you see on the income statement, which result in the company’s gains or losses. Cash flows provide more information about cash assets listed on a balance sheet and are related, but not equivalent, to net income shown on the income statement.
The financial statement allows credit officers to easily gain perspective into the applicant’s financial situation in order to make an informed credit decision. In many cases, the individual or couple may be asked to provide a personal guarantee for part of the loan, or may have to pledge some of the personal assets as collateral to guarantee the loan. A personal financial statement is a document or spreadsheet outlining an individual’s financial position at a given point in time. A personal financial statement will typically include general information about the individual, such as name and address, along with a breakdown of total assets and liabilities. The balance sheet is one of a company’s most important financial statements, because it gives investors a snapshot of the company’s financial health at any given moment in time.
The main financial statements of a company are known as the income statement, the balance sheet and the cash flow statement. Each document gives a viewpoint into the firm’s activities, but taken all together, these documents should provide an overall outlook on the company’s current activities and potential for future growth. The information is divided into the general classifications of assets, liabilities and equity.
What are the four basic financial statements?
Financial statements are reports that summarize important financial accounting information about your business. There are three main types of financial statements: the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Using the income statement in real life
But combined, they provide very powerful information for investors. And information is the investor’s best tool when it comes to investing wisely. Business-related assets and liabilities are not generally included in a personal financial statement unless the person is directly and personally responsible.
That is just one difference, so let’s see what else makes these fundamental reports different. Assets and liabilities are separated on the balance into short- and long-term accounts. Short-term assets include cash on hand, accounts receivable and inventory. Goods in inventory may be further separated into the amount of raw materials, work in progress, and finished goods ready for sale and shipping. Long-term assets are real estate, buildings, equipment and investments.
For example, the individual personally guaranteed a loan for their business. This is similar to cosigning, so this would be included on the personal financial statement. We can see the difference in what exactly each one reports.
- The income statement is one of the financial statements of an entity that reports three main financial information of an entity for a specific period of time.
- At the end of every financial period, a company must submit several statements that give a complete overview of the company’s activities.
Gross Profit: tells you how profitable your products are
It also provides a company with valuable information about revenue, sales, and expenses. These statements are used to make importantfinancialdecisions. Business owners often use accounting to measure their company’s financial performance. Accounting is responsible for recording and reporting a company’s financial transactions.
Assets
Short-term liabilities are bank loans, accounts payable, accrued expenses, sales tax payable and payroll taxes payable. Long-term liabilities are debts payable in more than one year. The equity portion of the balance sheet has all the company’s investor contributions and the accumulated retained earnings. Stockholder investments include common and preferred stock.
Essentially, it is a company’s account ledger, containing information about assets the company possesses, liabilities and obligations it needs to address, and owner equity in the company. Although the income statement and balance sheet have many differences, there are a couple of key things they have in common. Along with the cash flow statement, they make up three major financial statements.
Cash basis accounting accurately reports cash for the business owner, making the cash flow statement redundant. Although this brochure discusses each financial statement separately, keep in mind that they are all related.
And even though they are used in different ways, they are both used by creditors and investors when deciding on whether or not to be involved with the company. The income statement, often called aprofit and loss statement, shows a company’s financial health over a specified time period.
The income statement is one of the financial statements of an entity that reports three main financial information of an entity for a specific period of time. Those information included revenues, expenses, and profit or loss for the period of time. At the end of every financial period, a company must submit several statements that give a complete overview of the company’s activities. Generally, these statements are filed on a quarterly basis, though firms may elect to file these statements on a monthly or annual basis instead.
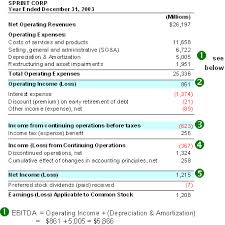
The end result of the income statement allows you to see the net income of the company, which you can analyze against the firm’s sales, debt and expenses if desired. The income statement is the primary financial statement for small business owners. The income statement lists all sales revenues, cost of goods sold and expenses for specific time period. Most income statements represent this information in a vertical format.
The income statement is the first of the financial statements to be created. The income statement lists all of a company’s revenues and expenses as it relates to income-generating activities. The revenues would be the sales that the company generates. The expenses would cover various operating items, such as the cost of inventory, utilities and rent related to the company’s working space, and advertising expenses, among others.
What are the 5 types of financial statements?
There are four main financial statements. They are: (1) balance sheets; (2) income statements; (3) cash flow statements; and (4) statements of shareholders’ equity. Balance sheets show what a company owns and what it owes at a fixed point in time.
The balance sheet formula
As a rule, the total amount of the company’s assets is equal to the total amount of its liabilities plus the owners’ equity in the company. This equation must always balance, with the same amount on each side of the sheet. The income statement is the most important of the financial statements, because it reveals basic truths about the financial performance of a company for a given reporting period. Beginning with sales, it subtracts expenses and arrives at a net profit or loss, and, in the case of publicly reported companies, an earnings-per-share figure for investors.
