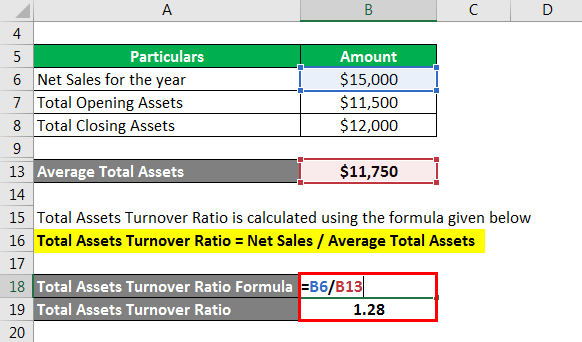
Average Total Assets
While the ratios for Linda’s Jewelry company may seem positive, we would need to compare this number to the asset turnover ratio of other companies in the jewelry industry to be sure. Shareholders’ equity is the net of a company’s total assets and its total liabilities.
These investments might include things such as building facilities, land, machinery and fleet vehicles. Managers and analysts use the return on assets ratio as a measure of performance. Comparisons between industrywide and internal prior year ratios might indicate a need for a company to use its assets more efficiently. The first key measure is the Return on Assets ratio, also known as ROA.
Average Total Assets Formula

Finally, increasing financial leverage means that the firm uses more debt financing relative to equity financing. Interest payments to creditors are tax-deductible, but dividend payments to shareholders are not.
You must create an account to continue watching
Liabilities are what a company owes, such as taxes, payables, salaries, and debt. The shareholders’ equity section displays the company’s retained earnings and the capital that has been contributed by shareholders.
If the firm takes on too much debt, the cost of debt rises as creditors demand a higher risk premium, and ROE decreases. Increased debt will make a positive contribution to a firm’s ROE only if the matching return on assets (ROA) of that debt exceeds the interest rate on the debt. The assets on the balance sheet consist of what a company owns or will receive in the future and which are measurable.
Since a company’s assets are either funded by debt or equity, some analysts and investors disregard the cost of acquiring the asset by adding back interest expense in the formula for ROA. Average total assets is defined as the average amount of assets recorded on a company’s balance sheet at the end of the current year and preceding year.
It’s the most commonly used benchmark for bank profitability since it measures the company’s return on investment in a format that is easily comparable with other institutions. ROA is a ratio of net income produced by total assets during a period of time. In other words, it measures how efficiently a company can manage its assets to produce profits. Return on equity (ROE) is a measure of financial performance calculated by dividing net income by shareholders’ equity.
Essentially, ROE will equal the net profit margin multiplied by asset turnover multiplied by financial leverage. Splitting return on equity into three parts makes it easier to understand changes in ROE over time. For example, if the net margin increases, every sale brings in more money, resulting in a higher overall ROE. Similarly, if the asset turnover increases, the firm generates more sales for every unit of assets owned, again resulting in a higher overall ROE.
This figure is most commonly used in comparison to the total sales figure for the current year, to determine the amount of assets required to support a certain amount of sales. This is a useful comparison, since a low asset level in comparison to sales implies that the management team is making highly efficient use of its assets in running the business. But if that company takes on financial leverage, its ROE would rise above its ROA. By taking on debt, a company increases its assets thanks to the cash that comes in.
ROE is a metric of how well the company utilizes its equity to generate profits. When a company consistently produces a low return on assets percentage, it may indicate a problem with its strategic management. If it purchases too much land, buildings and equipment, its assets and capital expenditures rapidly increase.
- The primary differentiator between ROE and ROA is financialleverage or debt.
Essentially, ROE only measures the return on a company’s equity, leaving out the liabilities. The more leverage and debt a company takes on, the higher ROE will be relative to ROA. Return on assets (ROA) is an indicator of how profitable a company is relative to its total assets.
The primary differentiator between ROE and ROA is financialleverage or debt. Although ROE and ROA are different measures of management effectiveness, the DuPont Identity formula shows how closely related they are. The DuPont formula, also known as the strategic profit model, is a common way to decompose ROE into three important components.
How do you calculate average total assets?
Average total assets can be calculated by using total assets value at the end of the current year plus total assets value at the end of the previous year and then divide the result by two.
Thus, a higher proportion of debt in the firm’s capital structure leads to higher ROE. Financial leverage benefits diminish as the risk of defaulting on interest payments increases.
Interpreting Asset Turnover Ratio
As with return on capital, a ROE is a measure of management’s ability to generate income from the equity available to it. ROE is also a factor in stock valuation, in association with other financial ratios. While higher ROE ought intuitively to imply higher stock prices, in reality, predicting the stock value of a company based on its ROE is dependent on too many other factors to be of use by itself. Net revenue is taken directly from the income statement, while total assets is taken from the balance sheet. If a company is in operation for more than one year, the average of the assets for each year must be calculated.
In corporate finance, the return on equity (ROE) is a measure of the profitability of a business in relation to the equity. Because shareholder’s equity can be calculated by taking all assets and subtracting all liabilities, ROE can also be thought of as a Return on Assets Minus Liabilities. ROE measures how many dollars of profit are generated for each dollar of shareholder’s equity.
Shareholders’ equity represents the net worth of a company and helps to determine its financial health. Shareholders’ equity is the amount of money that would be left over if the company paid off all liabilities such as debt in the event of a liquidation. ROE and ROA are important components in banking for measuring corporate performance.
What is included in average total assets?
To calculate the average total assets, add the total assets for the current year to the total assets for the previous year,and divide by two.
This might backfire if actual sales and income do not meet management’s growth projections. Management may also use the company’s assets poorly if it inappropriately disperses its production facilities and responsibilities. Consolidation or the integration of several functions, such as warehousing and order fulfillment, may be a more efficient solution. Companies use the return on assets (ROA) ratio to determine whether they are earning enough money from capital investments.
How to Calculate Asset Turnover Ratio: Formula & Example
But since shareholder equity equals assets minus total debt, a company decreases its equity by increasing debt. The way that a company’s debt is taken into account is the main difference between ROE and ROA. In the absence of debt, shareholder equity and the company’s total assets will be equal. ROE is especially used for comparing the performance of companies in the same industry.
Because shareholders’ equity is equal to a company’s assets minus its debt, ROE could be thought of as the return on net assets. Both ROA and return on equity (ROE) are measures of how a company utilizes its resources.
For the balance sheet to balance, total assets should equal the total of liabilities and shareholders’ equity. Remember total assets is also the sum of its total liabilities and shareholder’s equity. Both of these types of financing are used to fund the operations of the company.