Accrued Income
The offset entry to the debit entry of accrued payroll is a credit entry of either cash payments or payroll-related liabilities. A business that uses the accrual basis of accounting recognizes revenue and expenses in the accounting period in which they are earned or incurred, regardless of when payment occurs. This differs from the cash basis of accounting, under which a business recognizes revenue and expenses only when cash is received or paid. Two concepts, or principles, that the accrual basis of accounting uses are the revenue recognition principle and the matching principle.
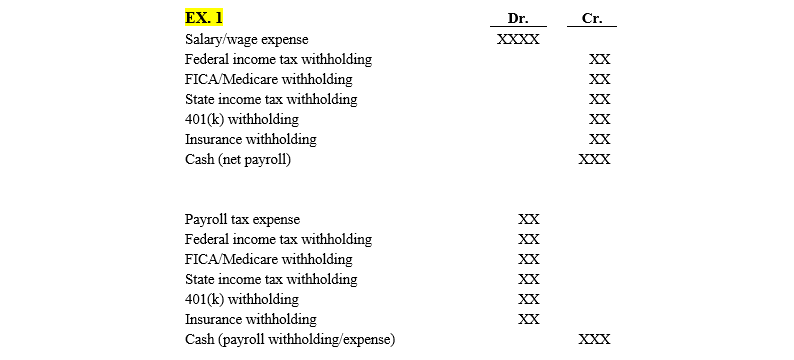
Although the accrual method of accounting is labor-intensive because it requires extensive journaling. The method is a more accurate measure of a company’s transactions and events for each period. This more complete picture helps users of financial statements to better understand a company’s present financial health and predict its future financial position. When the company’s accounting department receives the bill for the total amount of salaries due, the accounts payable account is credited. Accounts payable is found in the current liabilities section of the balance sheet and represents the short-term liabilities of a company.
Accruals cannot be made for depreciation or bad debt expense. Therefore, reversing accruals cannot be used for reversing depreciation or bad debt expenses.
An accrued expense is an expense that has been incurred, but for which there is not yet any expenditure documentation. In place of the expenditure documentation, a journal entry is created to record an accrued expense, as well as an offsetting liability (which is usually classified as a current liability in the balance sheet).
Once the payment has been made in the new year, the liability account will be decreased through a debit, and the cash account will be reduced through a credit. In double-entry bookkeeping, the offset to an accrued expense is an accrued liability account, which appears on the balance sheet. The offset to accrued revenue is an accrued asset account, which also appears on the balance sheet. Therefore, an adjusting journal entry for an accrual will impact both the balance sheet and the income statement. Accruals and deferrals are the basis of the accrual method of accounting, the preferred method by generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
An adjusting journal entry impacts at least one balance sheet account and one income statement account. In the case of payroll accrual, the accounts affected may be Accrued Wages and Salaries (balance sheet) and Wage and Salary Expense (income statement). At the end of a fiscal period a company records adjusting entries to recognize expenses which had been incurred, but not paid for yet. Note that we are talking about companies that apply accrual accounting here.
AccountDebitCreditCash AccountXAccrued Liability AccountXWhen the original entry is reversed (showing you paid the expense), it’s removed from the balance sheet. An example of an expense accrual involves employee bonuses that were earned in 2019, but will not be paid until 2020. The 2019 financial statements need to reflect the bonus expense earned by employees in 2019 as well as the bonus liability the company plans to pay out. Therefore, prior to issuing the 2019 financial statements, an adjusting journal entry records this accrual with a debit to an expense account and a credit to a liability account.
The entry for accrued revenue is typically a credit to the sales account and a debit to an accrued revenue account. Do not record any revenue accruals in the accounts receivable account, since that is reserved for trade receivables that are usually posted to the account through the billings module in the accounting software. For example, a company with a bond will accrue interest expense on its monthly financial statements, although interest on bonds is typically paid semi-annually. The interest expense recorded in an adjusting journal entry will be the amount that has accrued as of the financial statement date. A corresponding interest liability will be recorded on the balance sheet.
In the absence of a journal entry, the expense would not appear at all in the entity’s financial statements in the period incurred, which would result in reported profits being too high in that period. In short, accrued expenses are recorded to increase the accuracy of the financial statements, so that expenses are more closely aligned with those revenues with which they are associated.
- Accruals are revenues earned or expenses incurred which impact a company’s net income on the income statement, although cash related to the transaction has not yet changed hands.
- Accrual accounts include, among many others, accounts payable, accounts receivable, accrued tax liabilities, and accrued interest earned or payable.
Accrued payroll is entered as a debit entry to record the employee payroll expense, representing the amount of total earnings employees have accumulated for the work they do as of the end of an accounting period. Accrued payroll is reported as an operating expense in the income statement in the period in which it is incurred, regardless of whether companies have made any cash payments on any owed wages and salaries.
Reversing accruals are optional and can be implemented at any time because they do not affect the financial statements. Accruals can be used to match revenue, expenses and prepaid items to the current accounting period.
AccountingTools
The concept of accruals also applies in Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and plays a crucial role in accrual accounting. Under this method of accounting, earnings and expenses are recorded at the time of the transaction, regardless of whether or not cash flows have been received or dispensed. By doing this, a company can assess its financial position by factoring in the amount of money that it expects to take in rather than the money that it has received as of yet.
How to Calculate Payroll Accruals
A credit to cash reduces the balance in the cash account. If companies withhold any payroll taxes on behalf of employees, the cash payments are reduced by the amount of taxes to arrive at the net pay for employees. Companies then use another credit entry of payroll tax payable to offset the difference between the amount of total payroll and the amount of net pay.
A credit to the account of payroll payable increases the amount of payroll liability for the company. Therefore, the longer the time difference between when companies accrue their payroll and when they actually make payroll payments, the more the companies’ labor expenses are financed by their employees. Accruals are normally recorded by posting adjusting journal entries at the end of a period.
Companies that utilize cash accounting don’t use accruals and adjusting entries related to them. Accrued revenue is recorded when you have earned revenues from a customer, but have not yet billed the customer (once the customer is billed, the sale is recorded through the billing module in the accounting software). Accrued revenue situations may last for several accounting periods, until the appropriate time to invoice the customer. Nonetheless, accrued revenue is characterized as short-term, and so would be recorded within the current assets section of the balance sheet.
Comparisons Between Journal Entries
The use of accrual accounts greatly improves the quality of information on financial statements. Before the use of accruals, accountants only recorded cash transactions. Unfortunately, cash transactions don’t give information about other important business activities, such as revenue based on credit extended to customers or a company’s future liabilities. By recording accruals, a company can measure what it owes in the short-term and also what cash revenue it expects to receive. It also allows a company to record assets that do not have a cash value, such as goodwill.
Using the accrual method, an accountant makes adjustments for revenue that has been earned but is not yet recorded in the general ledger and expenses that have been incurred but are also not yet recorded. The accruals are made via adjusting journal entries at the end of each accounting period, so the reported financial statements can be inclusive of these amounts. If an accrual is recorded for an expense, you are debiting the expense account and crediting an accrued liability account (which appears in the balance sheet). Therefore, when you accrue an expense, it appears in the current liabilities portion of the balance sheet.
Is payroll an accrued expense?
The term accrual simply means accumulation. Payroll accrual refers to accrued salaries, wages, commissions, bonuses, benefits earned and payable to the employees. In simple terms, the liability arising from workers’ salary expense which has been incurred but not yet paid is called accrued payroll.
Try our payroll software in a free, no-obligation 30-day trial!
Accruals are revenues earned or expenses incurred which impact a company’s net income on the income statement, although cash related to the transaction has not yet changed hands. Accruals also affect the balance sheet, as they involve non-cash assets and liabilities. Accrual accounts include, among many others, accounts payable, accounts receivable, accrued tax liabilities, and accrued interest earned or payable. Because the company actually incurred 12 months’ worth of salary expenses, an adjusting journal entry is recorded at the end of the accounting period for the last month’s expense. The adjusting entry will be dated December 31 and will have a debit to the salary expenses account on the income statement and a credit to the salaries payable account on the balance sheet.