A Beginner’s Guide to The Accounting Cycle
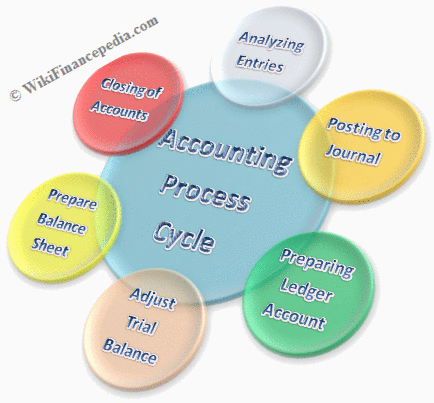
Keeping accurate financial documents is not an option. The accounting cycle is the system in which businesses record their transactions in order to prepare required financial statements. However, many business owners don’t understand this process fully, so we’re breaking it down in today’s post. At the end of an accounting period, Closing entries are made to transfer data in the temporary accounts to the permanent balance sheet or income statement accounts. Accounting cycle is a process of a complete sequence of accounting procedures in appropriate order during each accounting period.
Next, each transaction is recorded in a journal, a listing of financial transactions in chronological order. The journal entries are then recorded in ledgers, which show increases and decreases in specific asset, liability, and owners’ equity accounts.
If the accounting entries are recorded without error, the aggregate balance of all accounts having positive balances will be equal to the aggregate balance of all accounts having negative balances. Prepare a post-closing trial balance to verify that the total dollar amount of debits equals the total dollar amount of credits in the general ledger.
Via use of a balance sheet, they regularly log financial transactions that, over time, serve to present a snapshot of a business’s financial health and prognosticate its longevity. After journalizing and posting all adjusting entries, many businesses prepare another trial balance from their ledger and accounts.
These balances are transferred to next financial year as an opening balance. The accounting cycle refers to the process of generating financial statements. It begins with analyzing business transactions, recording them in journals, and posting them to ledgers.
It shows the balance of all accounts, including those adjusted, at the end of the accounting period. Therefore, the end result of this adjusted trial balance demonstrates the effects of all financial events that occurred during that particular reporting period. This is the act of transferring information from the journal to the ledger. Posting is needed in order to have a complete record of all accounting transactions in the general ledger, which is used to create a company’s financial statements.
BlackLine Accounting Process Automation solution improves the speed, accuracy, and reliability of the reconciliation to adjustment process by automating your routine and high-volume transactional processes. Based upon the system of debits and credits known as double-entry accounting, accountants use a general ledger to track money as it flows in and out of a business.
Computers have simplified many of these labor-intensive tasks. The accounting cycle refers to the process of generating financial statements, beginning with a business transaction and ending with the preparation of the report. The first step in the cycle is to analyze the data collected from many sources.
Prepare an adjusted trial balance to verify that the total dollar amount of debits equals the total dollar amount of credits in the general ledger. Adjusting entries are journal entries recorded at the end of an accounting period that alter the final balances of various general ledger accounts. These adjustments are made in order to more closely align the reported results and the actual financial position of a business. Adjusting entries follow the principles of revenue recognition and matching. The temporary income summary account then would be closed when preparing the financial statements.
Unadjusted Trial Balance
All transactions that have a financial impact on the firm—sales, payments to employees and suppliers, interest and tax payments, purchases of inventory, and the like—must be documented. The accountant must review the documents to make sure they’re complete. Using generally accepted accounting principles, accountants record and report financial data in similar ways for all firms. They report their findings in financial statements that summarize a company’s business transactions over a specified time period.
The Accounting Cycle: 9-Step Accounting Process
- This is a continuous process throughout the accounting period.2Posting in JournalOn the basis of the above documents, you pass journal entries using double entry system in which debit and credit balance remains equal.
- 1Collecting and Analyzing Accounting DocumentsIt is a very important step in which you examine the source documents and analyze them.
The ledger totals for each account are summarized in a trial balance, which is used to confirm the accuracy of the figures. These values are used to prepare financial statements and management reports. Finally, individuals analyze these reports and make decisions based on the information in them. Designed to complement existing financial systems, BlackLine fills the gaps left by ERP and CPM systems to help companies increase operational efficiency, real-time visibility, and control and compliance. This ensures end-to-end financial close management and accounting automation, and drives better decision-making across the business.
Accounting process is a combination of a series of activities that begin when a transaction takes place and ends with its inclusion in the financial statements at the end of the accounting period. DetailDebitCreditCash$11,670-Accounts receivable-0–Prepaid insurance2,420-Supplies3,620-Furniture16,020-Accounts payable-220Unearned consulting revenue-3,000Notes payable-6,000Mr. If the sum of the debit entries in a trial balance doesn’t equal the sum of the credits, that means there’s been an error in either the recording or posting of journal entries. At the end of the accounting period, atrial balanceis calculated as the fourth step in the accounting cycle. A trial balance tells the company its unadjusted balances in each account.
1Collecting and Analyzing Accounting DocumentsIt is a very important step in which you examine the source documents and analyze them. For example, cash, bank, sales, and purchase related documents. This is a continuous process throughout the accounting period.2Posting in JournalOn the basis of the above documents, you pass journal entries using double entry system in which debit and credit balance remains equal. This process is repeated throughout the accounting period.3Posting in Ledger AccountsDebit and credit balance of all the above accounts affected through journal entries are posted in ledger accounts.
With the help of trial balance, we put all the information into financial statements. With the result of these entries, the balance of all the accounts of income and expenditure accounts come to NIL.
Post-Closing Trial Balance
As mentioned earlier, the three major financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. In the double-entry accounting system, each accounting entry records related pairs of financial transactions for asset, liability, income, expense, or capital accounts. Recording of a debit amount to one account and an equal credit amount to another account results in total debits being equal to total credits for all accounts in the general ledger.
Point of sale technology can help to combine Steps 1 and 2, but companies must also track their expenses. The choice between accrual and cash accounting will dictate when transactions are officially recorded. Keep in mind, accrual accounting requires the matching of revenues with expenses so both must be booked at the time of sale.
Identifying and Analyzing Business Transactions
Ledger totals are then summarized in a trial balance that confirms the accuracy of the figures. Next the accountant prepares the financial statements and reports. The final step involves analyzing these reports and making decisions.
If debits equal credits, the accounting equation will balance. If the accounting equation balances, the financial statements will tie together. The time period principle requires that a business should prepare its financial statements on periodic basis. Therefore accounting cycle is followed once during each accounting period. Accounting Cycle starts from the recording of individual transactions and ends on the preparation of financial statements and closing entries.
The unadjusted trial balance is then carried forward to the fifth step for testing and analysis. The second step in the cycle is the creation of journal entries for each transaction.
*10. Reversing Entries: Optional step at the beginning of the new accounting period
Since we follow double entry system of accounts, the total of all the debit and credit balance as appeared in trial balance remains equal. Since in most of the cases, we used accrual basis of accounting to find out the correct value of revenue, expenses, assets and liabilities accounts, we need to do these adjustment entries. This process is performed at the end of each accounting period.6Adjusted Trial BalanceTaking into account the above adjustment entries, we create adjusted trial balance.